QCT QuantaGrid D54X-1U
The QCT QuantaGrid D54X-1U is the company’s high-volume 1U dual-socket server based on Intel Xeon Scalable. Currently, it uses the 4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable and the Intel Xeon Max series. Standard, it comes as an air-cooled package.
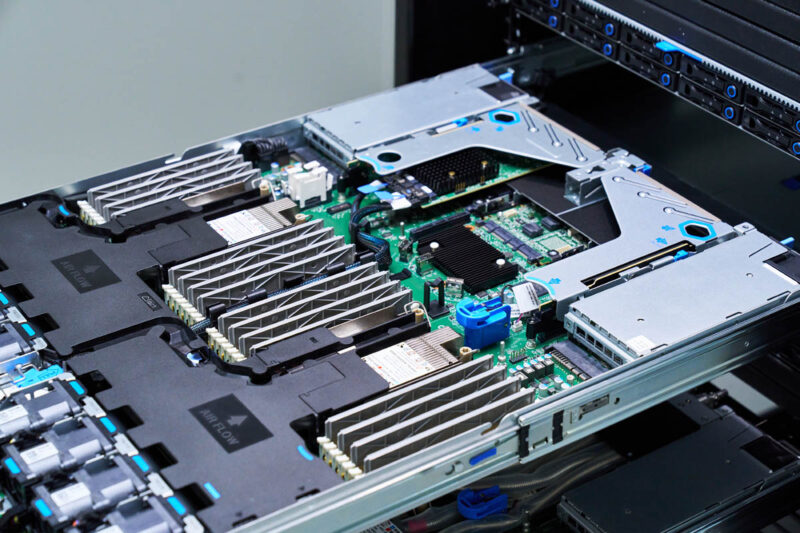

To cool today’s hot CPUs, 1U form factors are a challenge, so we need good airflow guides and often heatsink wings to keep CPUs cool.
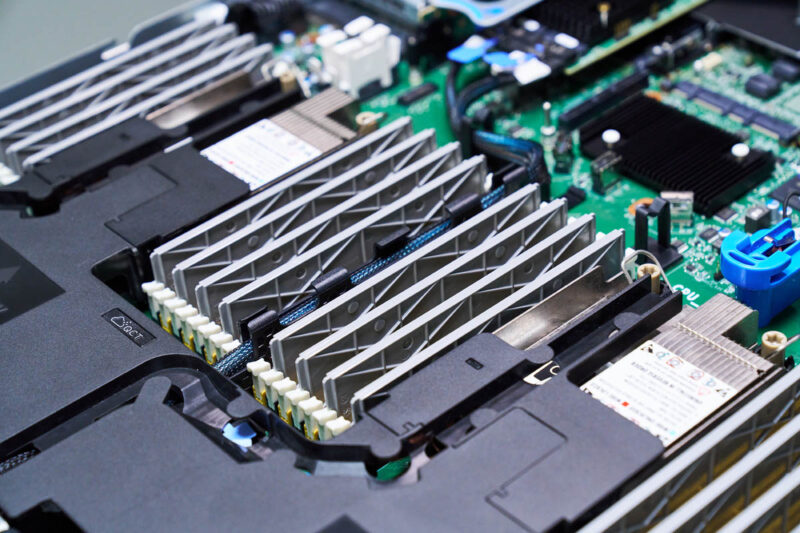
The air-cooled server we took photos of has blanks for DDR5 DIMM slots to help airflow, but it could boot because it was using the Intel Xeon Max series. If you want to learn more about these HBM2e-equipped parts designed for HPC, you can also see our video:
The other option, with the QuantaGrid D54X-1U, is liquid cooling. That is the option for the QoolRack.
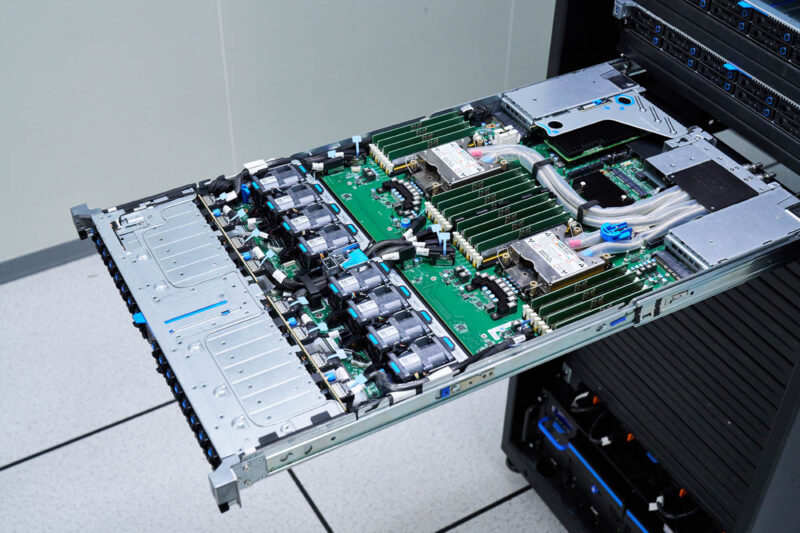

One can see that we added liquid cooling components but removed the large heatsinks and airflow guides.
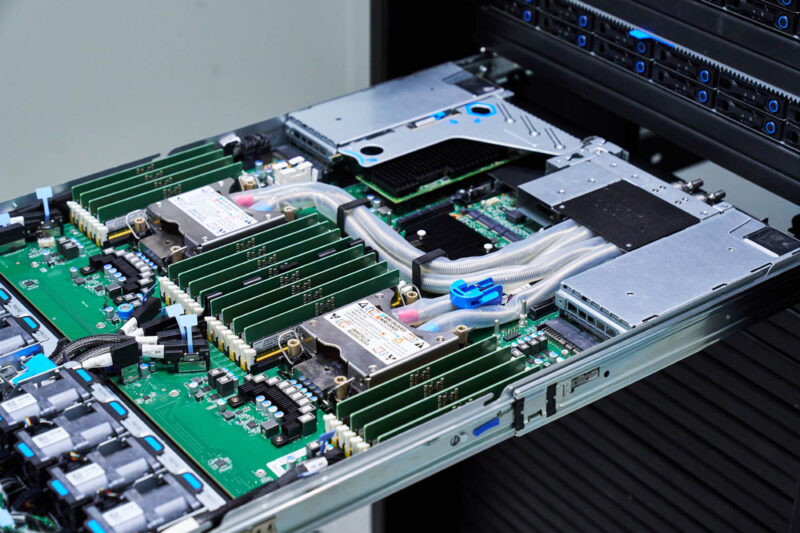

Here is one of the sockets with the liquid cooling block.
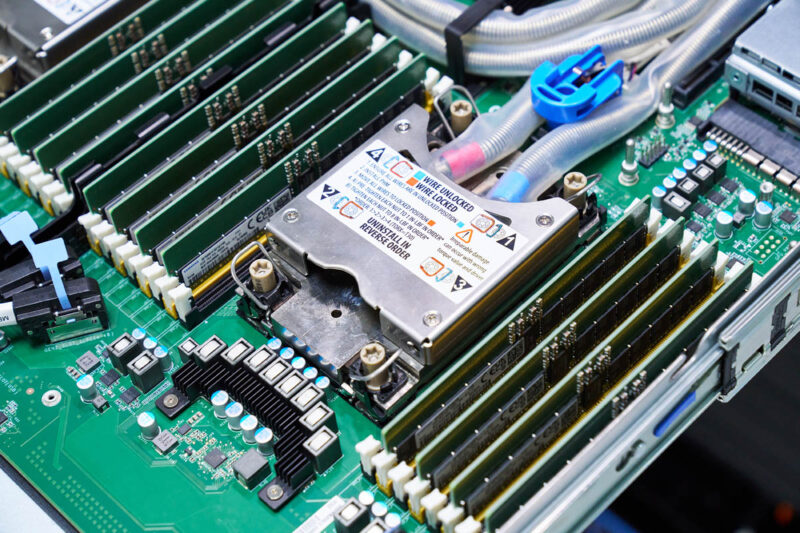
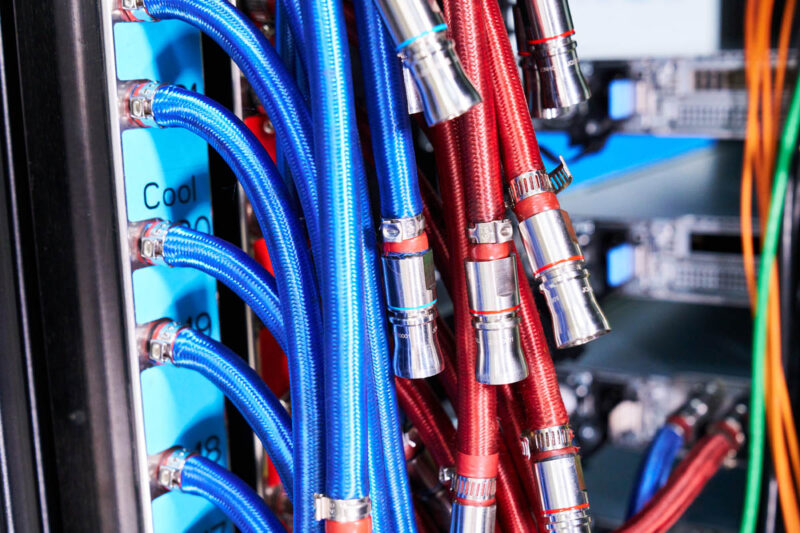
Here is the other. Luckily, something that vendors standardized on is blue, which means cooler fluid, and red, which means warmer fluid.
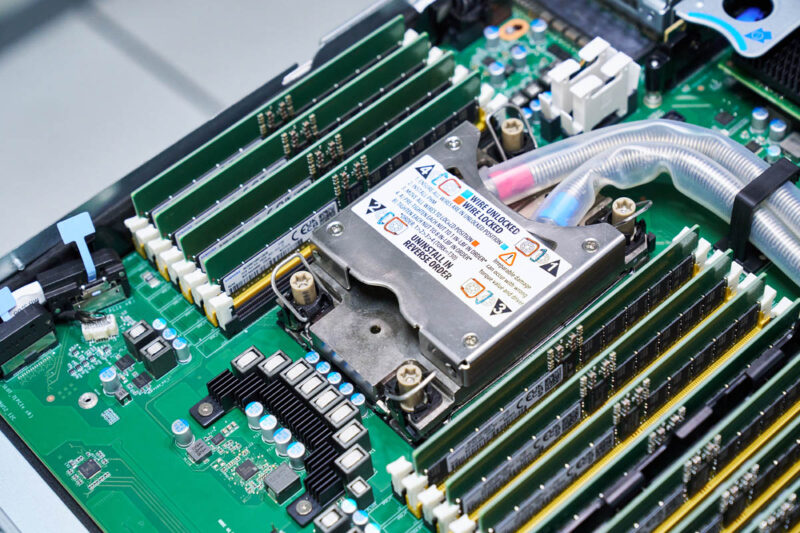
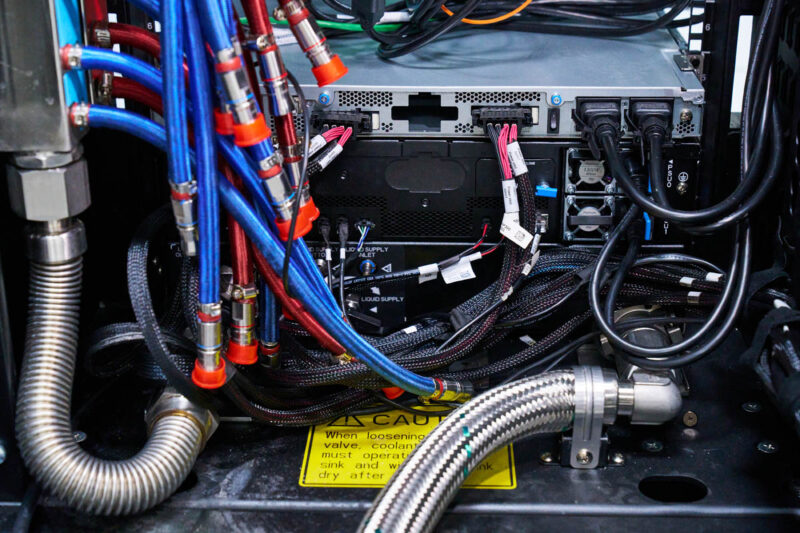
The tubes pass behind the CPUs and to the rear through one of the expansion slots.
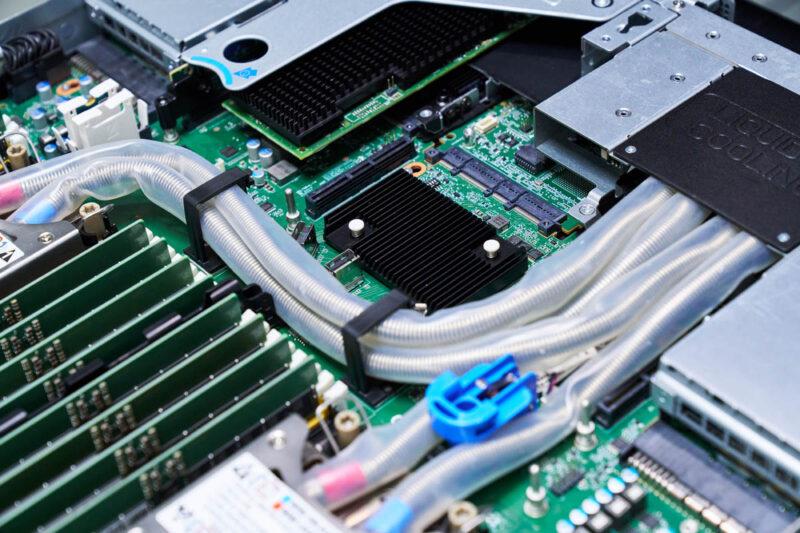
On the subject of the rear of the QoolRack, let us get to that next.
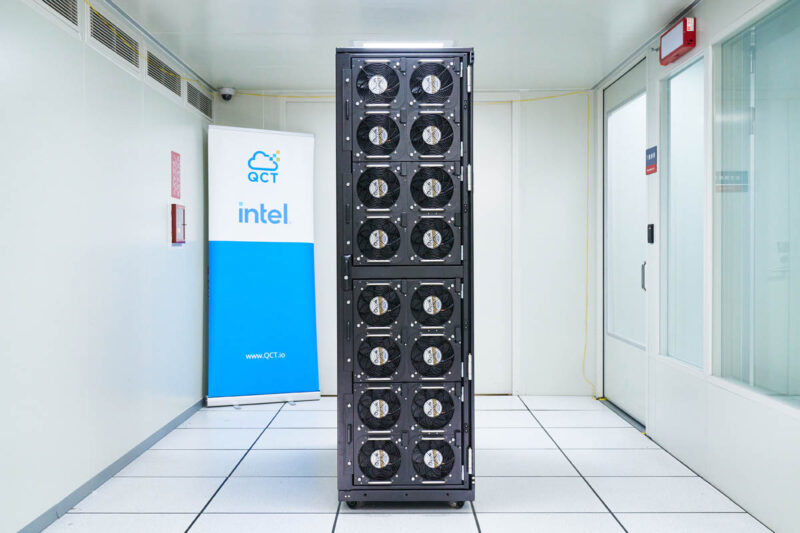
Quanta QCT QoolRack Liquid Cooling Rack Rear
Looking at the rear of the rack, it is a giant fan wall.

On the other side of the rack door is a large heat exchanger. QCT can also use facility water, but this setup has a big advantage. Using a rear door heat exchanger, one can install a liquid cooling rack into a standard data center without bringing facility water to the rack.
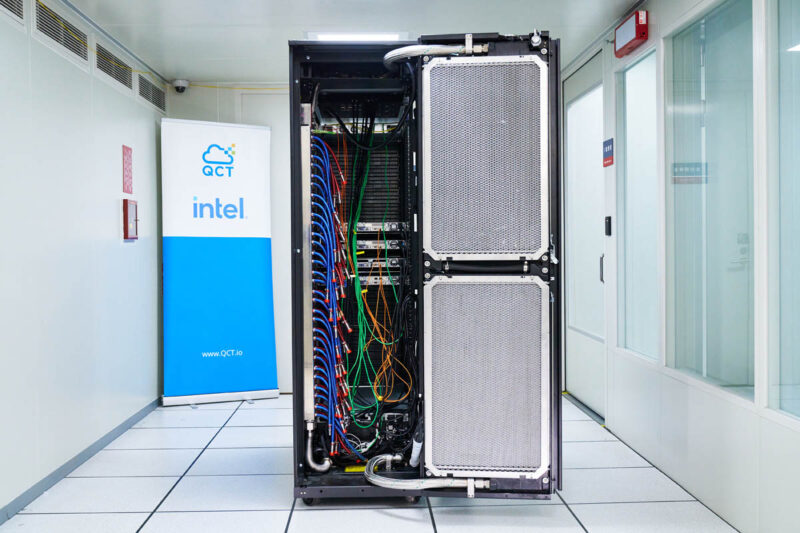

The rear door heat exchanger is like a scaled-up version of a liquid-cooled PC’s radiator. Instead of dealing with 0.5-1kW, these are designed for tens of kW of power in a rack.
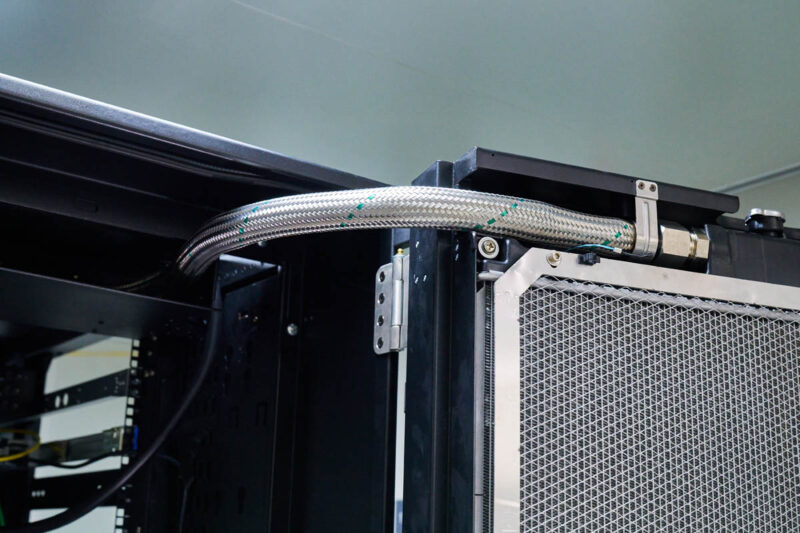

The tubes feeding the heat exchanger are huge.
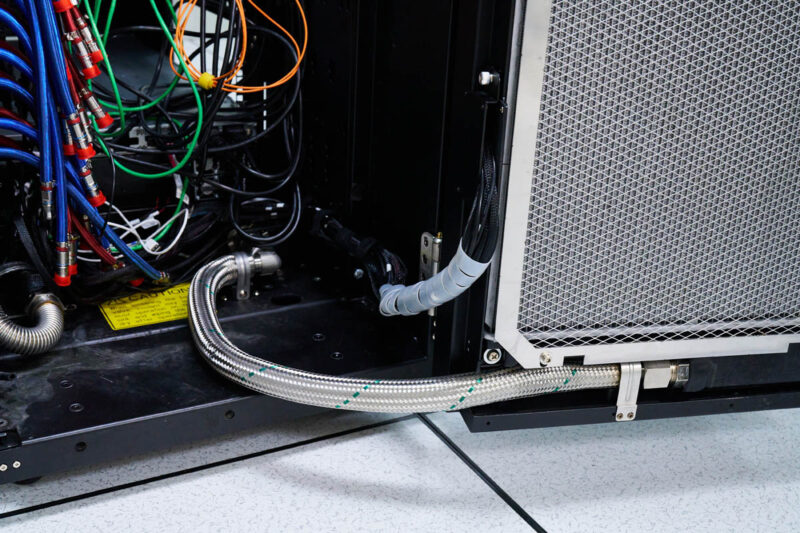

On the side of the rack, there are the rack manifolds. Each manifold has quick disconnects on the server side. Again, blue for cooler liquid and red for warmer liquid.

Something immediately notable is that the connections from the manifold to the rear of the server are fixed on the manifold. We see some designs in the market use this approach while others have tubes with quick disconnect fittings on both ends.
Here is a look at the tubes from the rack manifold that connects to the rear of a QuantaGrid D54X-1U server. One can see that the liquid cooling takes up an expansion slot.

The CDU on the bottom of the chassis pumps fluid through the servers and exchanges it to move heat. We can see that CDU here:

Next, let us get to the performance.




Now show us the GPU version