NVIDIA Tesla T4 Compute Related Benchmarks
We are going to compare the NVIDIA Tesla T4 to our growing data set. We do not have the 8x Tesla V100 and 8x Tesla P100 SXM2 results in here since those are different classes of systems.
Geekbench 4
Geekbench 4 measures the compute performance of your GPU using image processing to computer vision to number crunching.
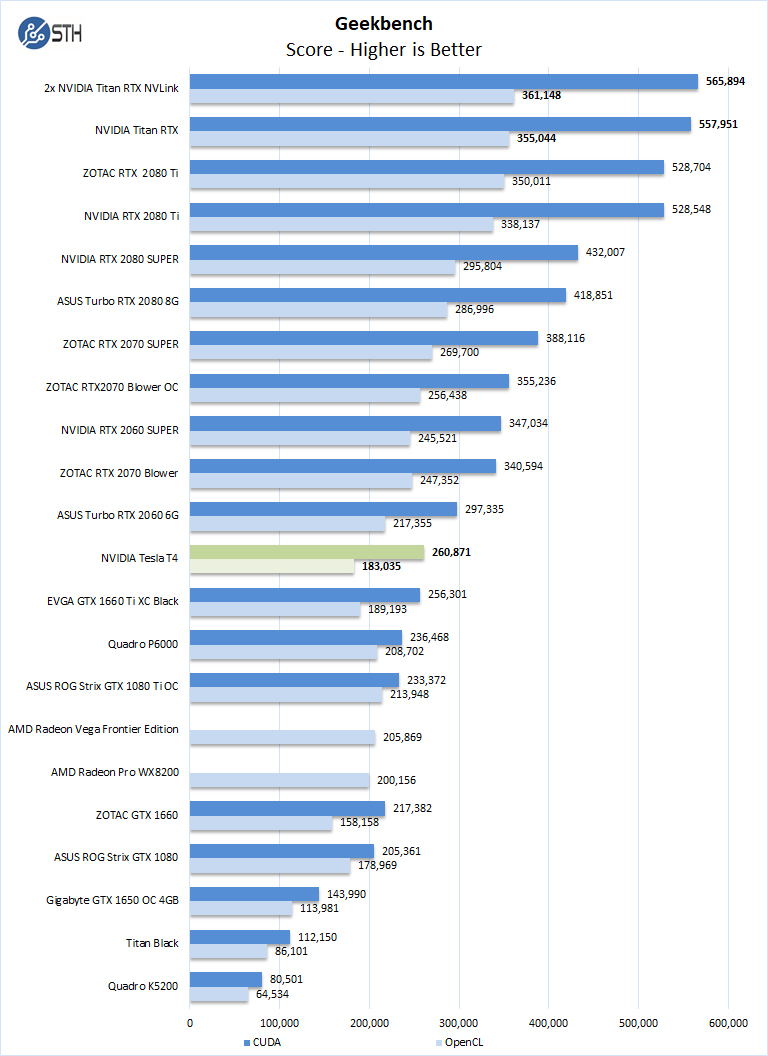
Our first compute benchmark we see the NVIDIA Tesla T4 achieves results between the ASUS Turbo GeForce RTX 2060 Blower and the EVGA GeForce GTX 1660 Ti XC Black. With CUDA support, it out-performs the higher-power AMD offerings.
LuxMark
LuxMark is an OpenCL benchmark tool based on LuxRender.
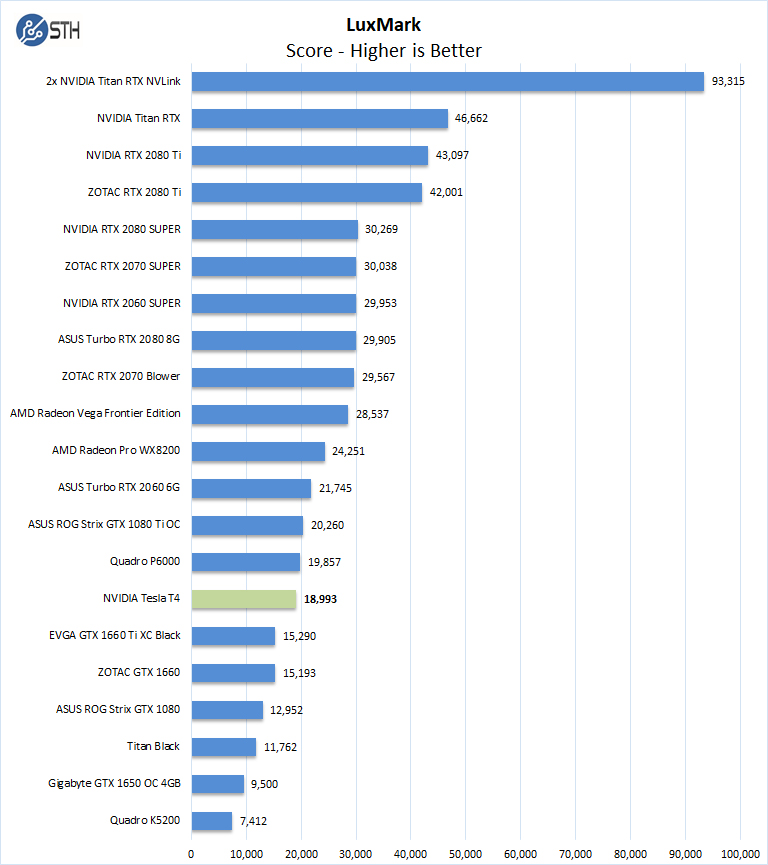
We were disappointed in the LuxMark results for the NVIDIA Tesla T4 compared to other Turing architecture cards. On the other hand, for those GeForce 1080 Ti fans, this is a great example of where the architectural shift means a fairly massive performance per watt gain over Pascal.
AIDA64 GPGPU
These benchmarks are designed to measure GPGPU computing performance via different OpenCL workloads.
- Single-Precision FLOPS: Measures the classic MAD (Multiply-Addition) performance of the GPU, otherwise known as FLOPS (Floating-Point Operations Per Second), with single-precision (32-bit, “float”) floating-point data.
- Double-Precision FLOPS: Measures the classic MAD (Multiply-Addition) performance of the GPU, otherwise known as FLOPS (Floating-Point Operations Per Second), with double-precision (64-bit, “double”) floating-point data.
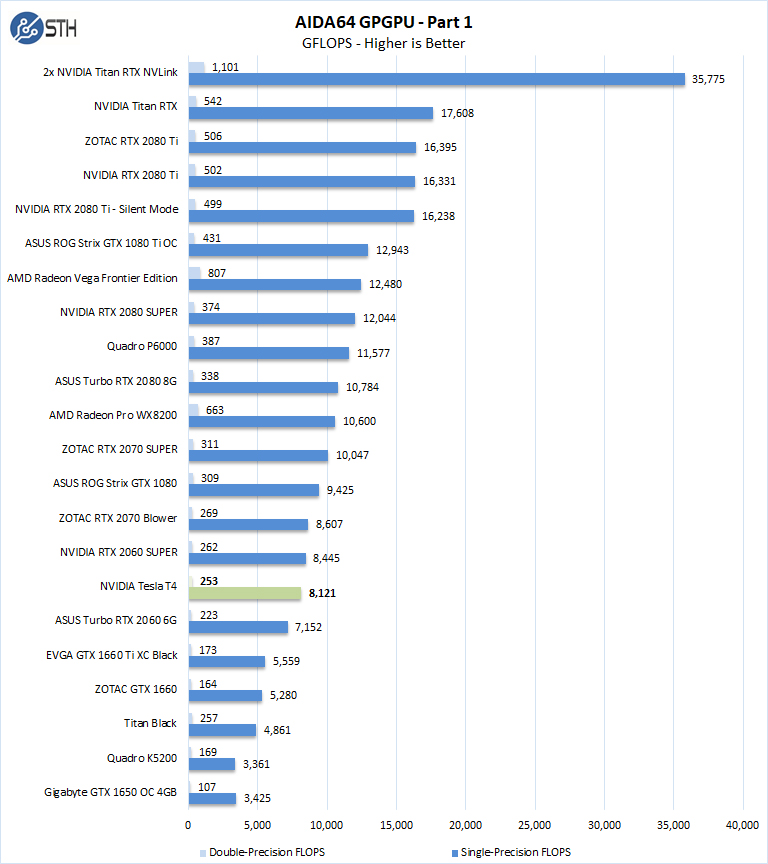
The next set of benchmarks from AIDA64 are:
- 24-bit Integer IOPS: Measures the classic MAD (Multiply-Addition) performance of the GPU, otherwise known as IOPS (Integer Operations Per Second), with 24-bit integer (“int24”) data. This particular data type defined in OpenCL on the basis that many GPUs are capable of executing int24 operations via their floating-point units.
- 32-bit Integer IOPS: Measures the classic MAD (Multiply-Addition) performance of the GPU, otherwise known as IOPS (Integer Operations Per Second), with 32-bit integer (“int”) data.
- 64-bit Integer IOPS: Measures the classic MAD (Multiply-Addition) performance of the GPU, otherwise known as IOPS (Integer Operations Per Second), with 64-bit integer (“long”) data. Most GPUs do not have dedicated execution resources for 64-bit integer operations, so instead, they emulate the 64-bit integer operations via existing 32-bit integer execution units.
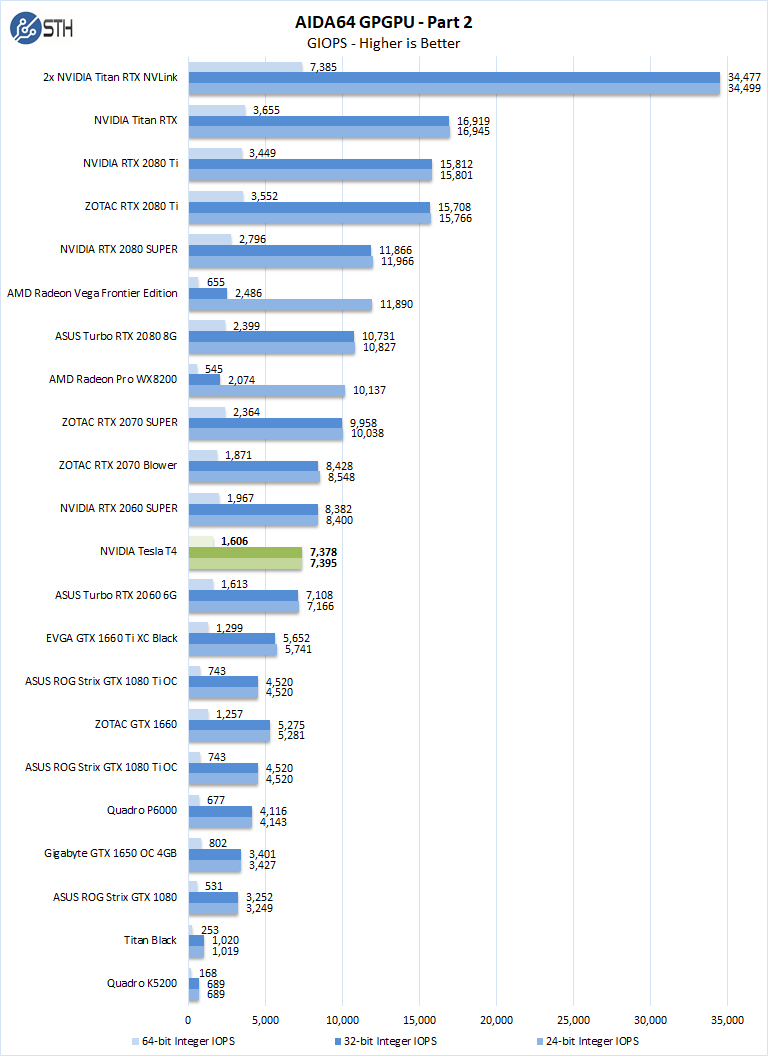
The take away here is the NVIDIA Tesla T4 archives near NVIDIA RTX 2060 SUPER performance. If you look at the execution units of both cards and clock speeds, you can see that the Tesla T4 will generally be at this level, if not a bit lower.
NVIDIA Tesla T4 Rendering Related Benchmarks
OctaneRender 4
OctaneRender from Otoy is an unbiased GPU renderer using the CUDA API. The latest release, OctaneRender 4, introduces support for out of core geometry. Octane is available as a standalone rendering application, and a demo version is available for downloaded from the OTOY website here.
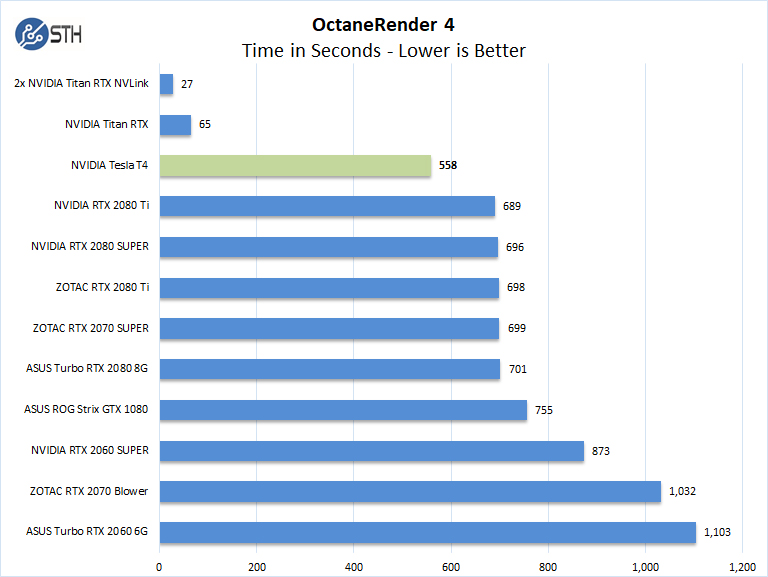
With OctaneRender, we have the ability to select which graphics card we want to run our test on, in this case, the NVIDIA Tesla T4. We should note that one can select all GPUs or just one which works well for multi-GPU systems and different workloads run at the same time. With OctaneRender the NVIDIA Tesla T4 shows faster than the NVIDIA RTX 2080 Ti, as the Telsa T4 has more memory to load in the benchmark data.
On a performance per watt basis, excluding the Titan RTX, the Tesla T4 is a clear winner here.
Next, we are going to look at the NVIDIA Tesla T4 with several deep learning benchmarks.




Another great review William
Great review, but I think what’s missing (or perhaps wasn’t known back then), is, that the T4 supports vGPUs according to official specs. Now it’s not easy to get it to work and normally it implies licensing fees, but not every card supports vGPUs. The T4 however does.