Kubernetes is an open-source orchestration system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Kuberenetes 1.11 is the second Kubernetes release in 2018 and it packs a few new features we know folks have been waiting for. Two big features in this release are now considered GA, CoreDNS and IPVS-based load balancing. If you do not have a Kubernetes cluster or at least a project in your organization’s pipeline at this point, it is time to jump on the bandwagon. Kubernetes is one of the most powerful forces in datacenters today.
We covered how Kubernetes won the container wars in Kubernetes Wins! Docker Acquiesces and Adopts Kubernetes. How Red Hat buys CoreOS in Kubernetes container ecosystem play. If you are a deep learning/ AI researcher a great announcement by NVIDIA recently about finally supporting Heterogeneous GPU Kubernetes Clusters. This is a big deal in the server ecosystem.
CoreDNS Cluster DNS
DNS is a service that needs to scale in a container orchestration environment. CoreDNS is the new cluster DNS option that is written in the Go programming language. The service was developed for better Kubernetes API integration and extensibility. While not the sexiest part of Kubernetes, DNS is a foundational element that the project is upgrading with 1.11.
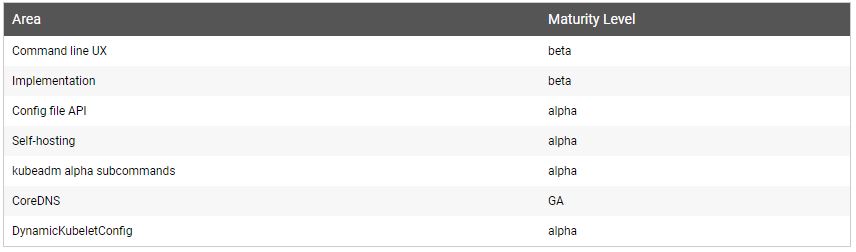
CoreDNS is integrated into the popular kubeadm tool for bootstrapping Kuberenetes clusters. (See here.)
IPVS-based Load Balancing
The IP Virtual Server (IPVS) load balancing is kernel based and fast. The feature is now GA in Kubernetes 1.11 and available for production traffic, but it is not set by default. We expect the cluster load balancing in the Kuberenetes Service model to have improved performance and scalability with the IPVS load balancing switch.
More Information
If you want to learn more about the Kubernetes 1.11 release, here is the official announcement. Kubernetes can be found on GitHub here. If you are looking for the kubeadm tool, go here.