At STH, we have the largest collection of Intel Xeon D benchmarks on the Internet yet we have a few chips that we have not yet published benchmarks on. One of those chips is the Intel Xeon D-1557. The final “7” digit tells us that it is a lower power storage-focused chip. We will have a bigger review of the mITX platform we used for this review shortly, but we did want to publish initial benchmarks of the Intel Xeon D-1557 which is a 12 core 18MB L3 cache chip. Clock speeds are sacrificed to keep a 45w TDP. The Intel Xeon D-1557 has a 1.5GHz base clock and a 2.1GHz maximum turbo clock. On the other hand, it runs at less than half the TDP of the Intel Xeon E5-2650 V4 (12 core 105W TDP) chip, and includes a dual 10GbE MAC in the 45w TDP envelope.
Test Configuration
Our test platform was not our standard platform. We did these benchmarks on a system we had in the DemoEval lab.
- CPU: Intel Xeon D-1557
- Platform: Supermicro X10SDV-12C-TLN4F+
- SSD: Intel DC S3700 400GB
- RAM: 4x 32GB DDR4 RDIMMs
Overall, the platform is extremely compact for the amount of processing power it gives.

Intel Xeon D-1557 Benchmarks
For our testing we are using Linux-Bench scripts which help us see cross platform “least common denominator” results. We are using gcc due to its ubiquity as a default compiler. One can see details of each benchmark here. We are likely going to update the Linux-Bench in the near future with a few new tests as well as an even simpler to use/ faster revision, but for now, we are using our old Ubuntu 14.04.4 version. If you want to see example results, here is one run on Linux-Bench.
Python Linux 4.4.2 Kernel Compile Benchmark
This is one of the most requested benchmarks for STH over the past few years. We (finally) have a Linux kernel compile benchmark script that is consistent. Expect to see this functionality migrate into Linux-Bench soon (we are just awaiting the parser work on it.) The task was simple, we have a standard configuration file, the Linux 4.4.2 kernel from kernel.org, and “make” with every thread in the system. We are expressing results in terms of complies per hour to make the results easier to read.
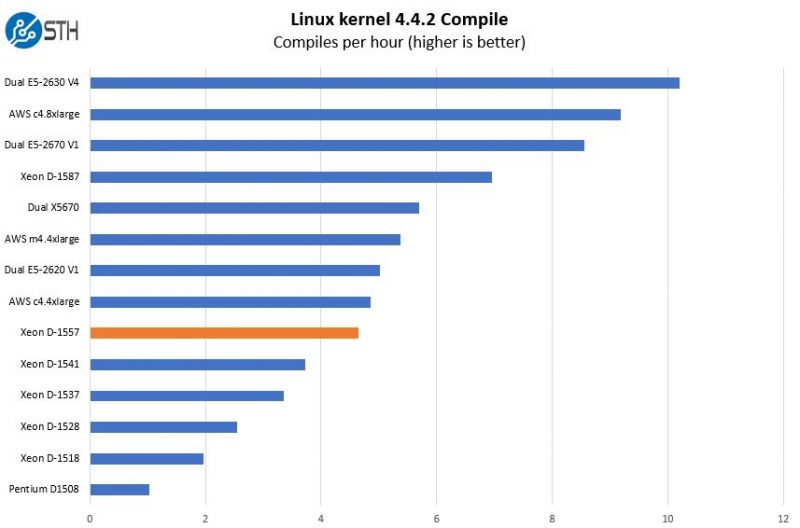
From a raw CPU compute perspective, this 45w TDP part is performing well above that of the Intel Xeon D-1541 and is competitive with older generation dual CPU systems such as the dual Xeon E5-2620 V1 system. The perspective is that it is realistically using close to 1/4 the power of the dual E5-2620 V1 system.
c-ray 1.1 Performance
We have been using c-ray for our performance testing for years now. It is a ray tracing benchmark that is extremely popular to show differences in processors under multi-threaded workloads.
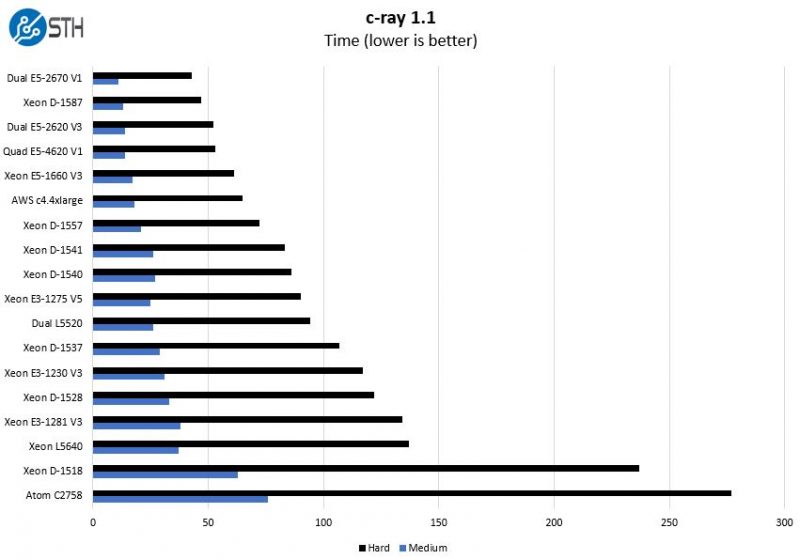
Here again we see the trend in highly multi-threaded benchmarks that the Intel Xeon D-1557 can push ahead of the much higher clock, but lower core count, Xeon D-1541.
7-zip Performance
7-zip is a widely used compression/ decompression program that works cross platform. We started using the program during our early days with Windows testing. It is now part of Linux-Bench.
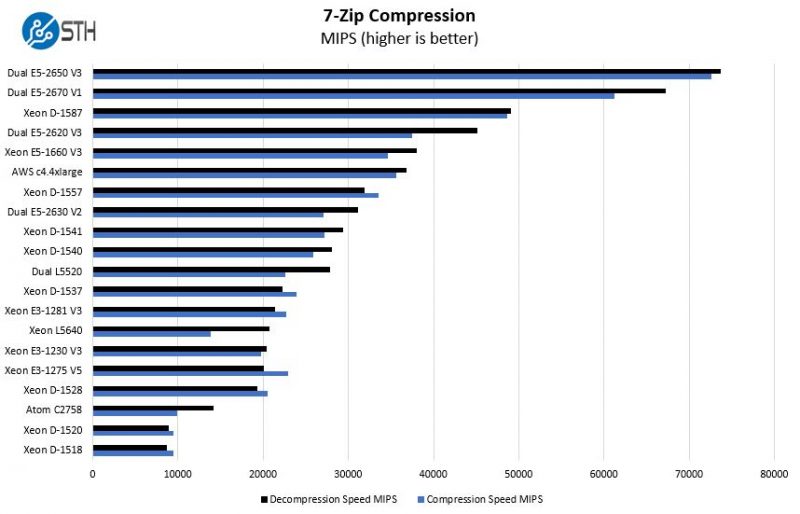
We are using a fairly wide comparison set here to show where the Intel Xeon D-1557 falls. We can see that the Intel Xeon D does perform very well in this test keeping pace even with a dual Intel Xeon E5-2630 V2 system.
NAMD Performance
NAMD is a molecular modeling benchmark developed by the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. More information on the benchmark can be found here.
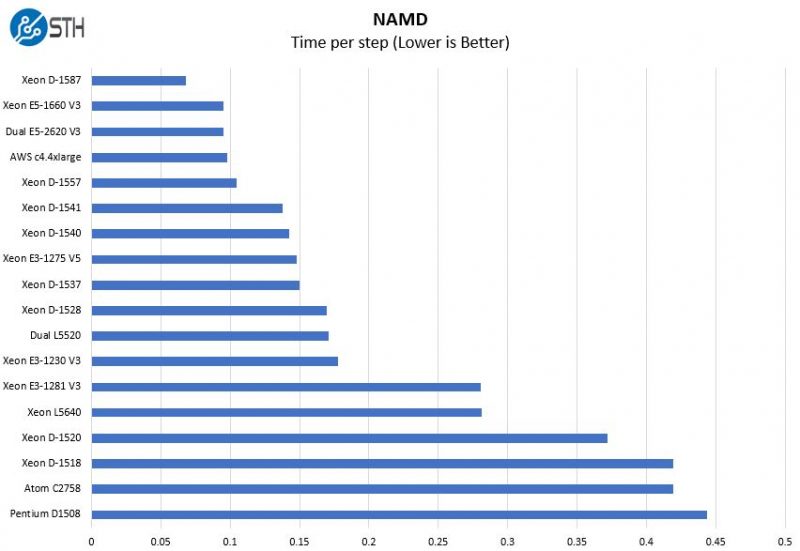
The Xeon D systems are not well suited to doing scientific research tasks. They do highlight multi-threaded performance.
Sysbench CPU test
Sysbench is another one of those widely used Linux benchmarks. We specifically are using the CPU test, not the OLTP test that we use for some storage testing.
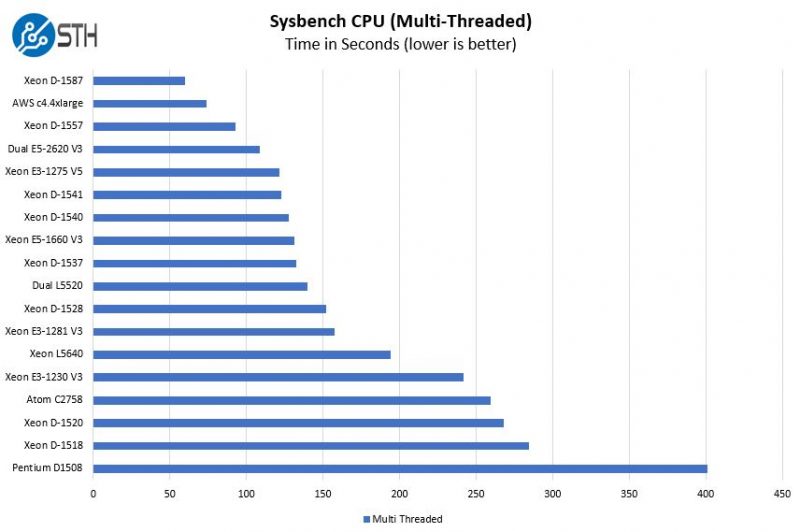
Again, we can see a very strong performance here from a low power part.
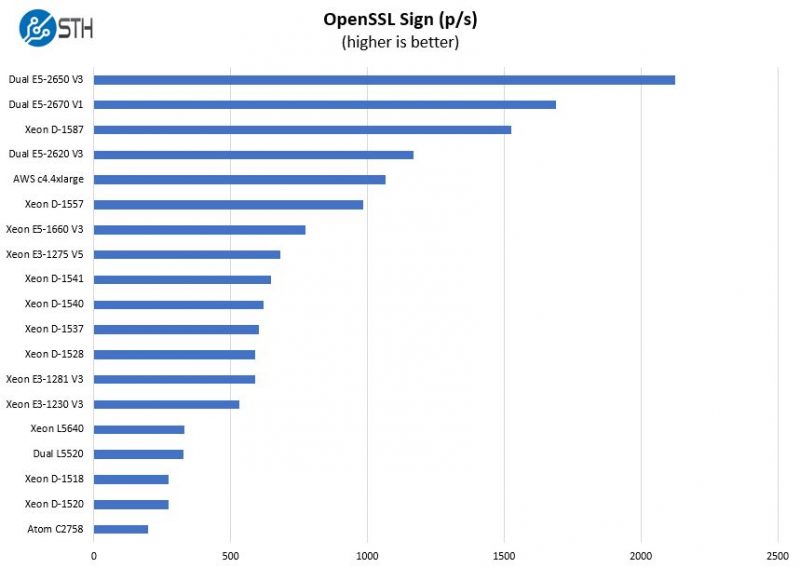
OpenSSL Performance
OpenSSL is widely used to secure communications between servers. This is an important protocol in many server stacks. We first look at our sign tests:
Moving to the verify results:
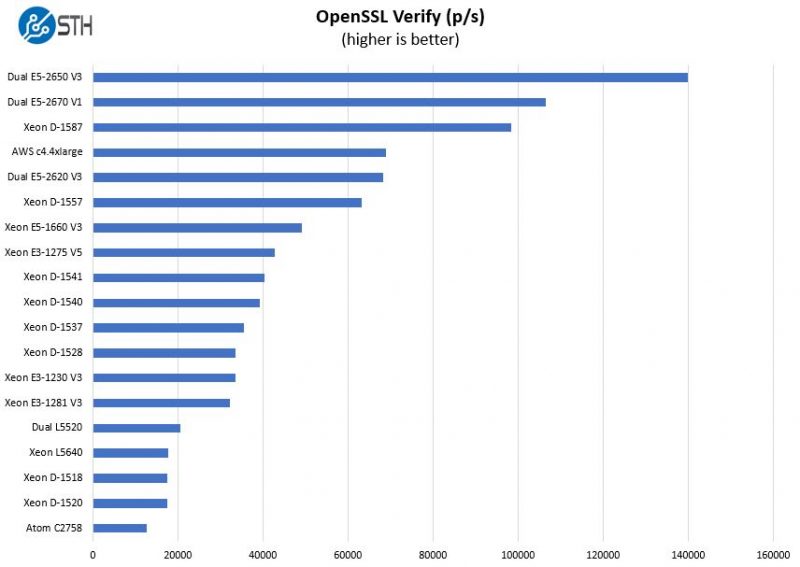
Our OpenSSL tests do tend to put a bit more emphasis on single thread performance while still scaling well with mutli-threading. We can see the D-1557 is scaling well.
UnixBench Dhrystone 2 and Whetstone Benchmarks
Of course, these chips are not meant for heavy compute but we pick out the UnixBench 5.1.3 Dhrystone 2 and Whetstone results to show some of the raw performance they are capable of. UnixBench is widely used so it is a good comparison point.
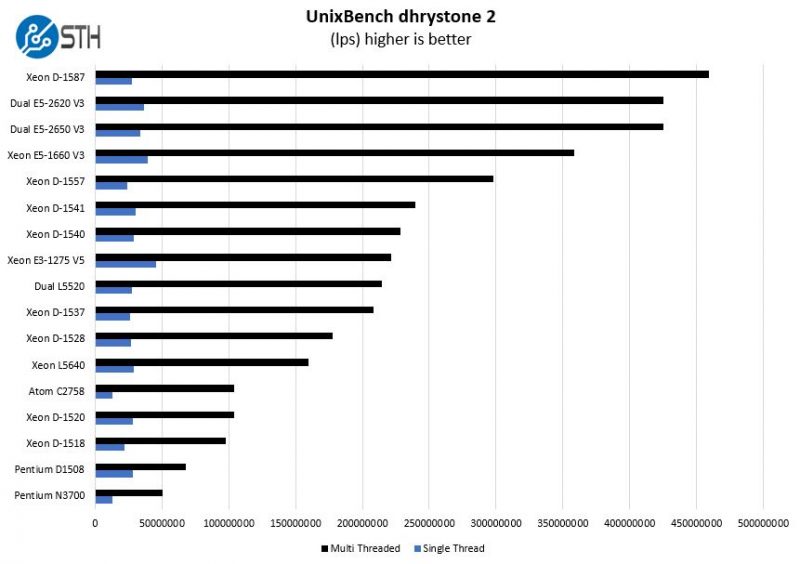
As we increase the core counts the multi-threaded performance dominates the chart scale. In single-threaded benchmarks the Intel Xeon D-1541 crushes the D-1557 at the same TDP. The D-1557 does pull ahead with multi-threaded results.
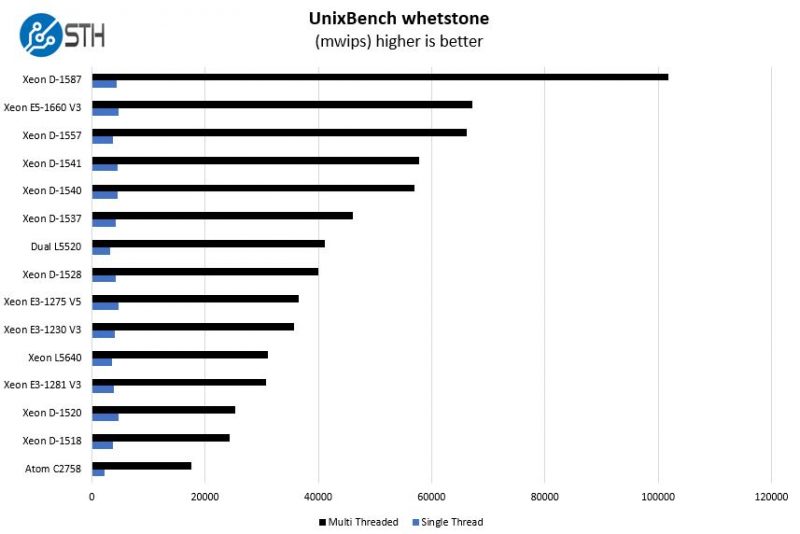
Again we see significantly stronger performance in single-threaded D-1541 performance over D-1557.
Conclusion
Part of STH’s hosting cluster is actually a number of 1U Intel Xeon D servers. We purchased many of the Intel Xeon D-1540 and D-1541 based platforms for the cluster because it provides solid single and multi-threaded performance. The Intel Xeon D-1557 performance is slightly different. It performs well on multi-threaded workloads but suffers on single-threaded tasks. We wanted to highlight this difference as the chips have the same TDP. The Intel Xeon D-1541 suggested pricing is about 2/3rds of the D-1557 pricing. While in multi-threaded tasks the D-1557 has a clear advantage we would recommend the D-1541 for general purpose performance due to its solid single-threaded performance.





1537 or 1557?