Something that we typically see as a challenge for building and operating AI clusters is managing all of the compute resources, users, data, and models through training and inference. This operations work may not seem as exciting as discovering a new method to solve a deep learning problem, but doing AI cluster operations well is important for scaling a shared resource within an organization. Inspur AIStation is designed to manage that lifecycle. We had some time to get hands-on with the solution and see how it operates. I also had the opportunity to ask a few questions of Liu Jun the head of AI at Inspur about the new product.
Hands-on with Inspur AIStation Background
Inspur has a test cluster in the Shandong province in China that I was able to get access to using a Cisco VPN. I do not know where exactly the cluster was, but I used a mental picture that this Inspur building in Jinan (2nd largest city and capital of the Shandong province) is where the test cluster resided. This was not the same Inspur campus as the Inspur Intelligent Factory we toured while there in 2019. Since many of our readers are from outside China and have never been to Shandong, for some perspective Jinan is roughly the same population as New York City.

If you have never heard of Jinan, but you have heard of New York City, that is exactly why I wanted to highlight AIStation. Inspur is the #3 server vendor in the world and sells around half of the AI servers in China. While Inspur sells to hyperscalers, one of its key competencies is AI servers such as the Inspur Systems NF5468M5 and Inspur NF5488M5 we reviewed recently. AIStation is the company’s offering to help manage large fleets of AI training and inferencing servers, along with the data and users.
AIStation is, at its root, a Kubernetes-based cluster solution. What Inspur has done is to unify many of the common tools and tasks one needs to address when running AI clusters. For example, it can manage users, groups, permissions, and quotas. It can manage data associated with each user or group as well as the permissions and storage for that data. It also can manage development work along with scheduling resources on the cluster. Another aspect we will cover is some of the monitoring and alerting at both the job, user, and node levels. Let us get into it.
Hands-on with Inspur AIStation: Admin View
We are not going through every screenshot here. Instead, I picked a number of screenshots that I wanted to talk about. First, I wanted to talk about the administrative side, before getting to what a user would see in the system. The solution is very modern, built on Kubernetes and containers. If you compare this to a lot of legacy GPU/ HPC/ AI scheduling systems, you can see that this is being done more in the spirit of modern architecture.
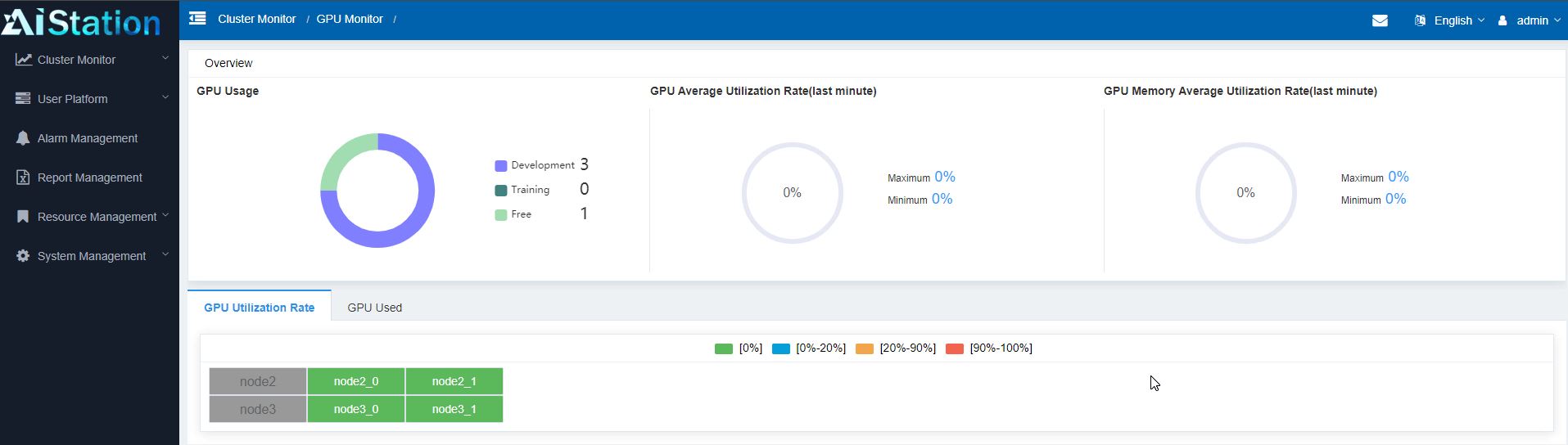
Once AIStation is running on the back-end, most of the day-to-day administrative work can be done using scripts or through the web GUI. For example, one can drill into individual nodes to see their loads, their hardware configurations, and even trace chains from the user, to the container, to the hardware they are running on down to the individual GPU level.
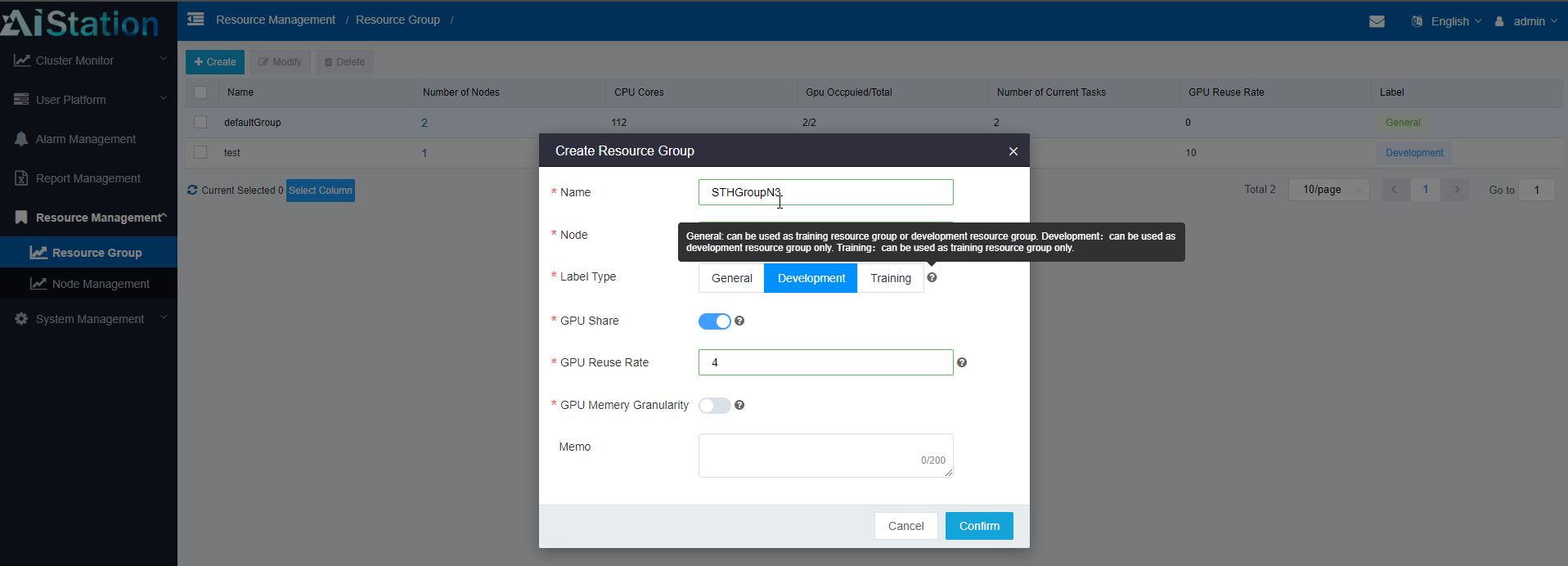
Although our test cluster only had a few nodes, we have heard that AIStation is already deployed with clusters of hundreds and over a thousand nodes. As the node count scales, creating resource groups can become more important. One can create groups of resources, designate them for development, training, or both (general) use. One can also set some of the higher-level management and reservation properties for the group here.
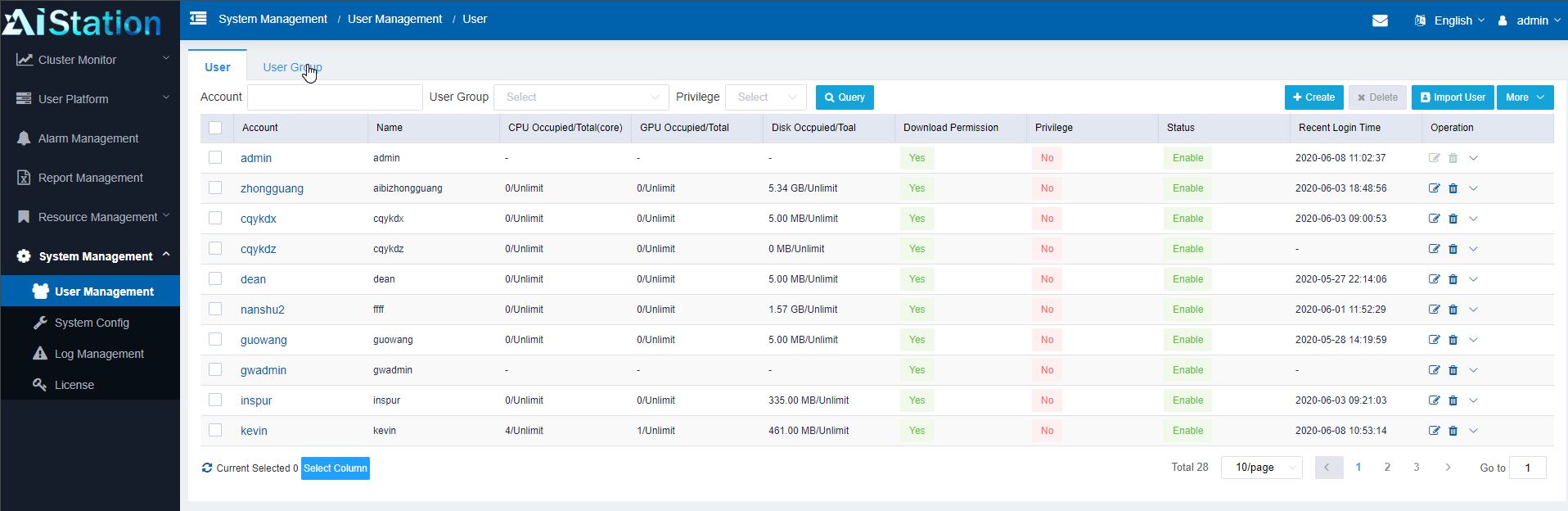
Along with creating groups of hardware, perhaps the more important aspect is creating users and user groups. Here one can create users or integrate with an existing user directory tool. Users can then be given access to different resources, storage quotas, GPU quotas, and more. This is important because one may have an intern that the company does not want to use an entire cluster 100% or having access to sensitive training data/ models. Conversely, perhaps a group of superstar deep learning folks run an internal consulting group and need access to everything and the company wants to prioritize their work. A big part of the AIStation value proposition is being able to manage this all through a single system.
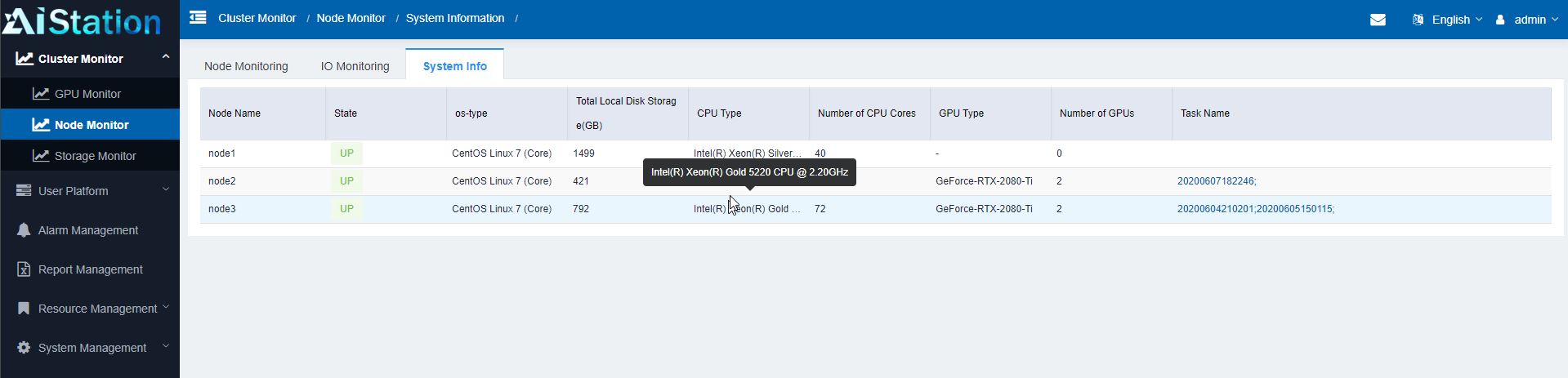
Admins can also have access to the entire stack (depending on privileges) to help ongoing operations. For example, an admin may be asked why a job is running slowly. That admin can use the monitoring tool to find the user, their jobs, and the specific container that is in question. From there, the admin can even go directly into the hardware to see if it is an underlying hardware issue.
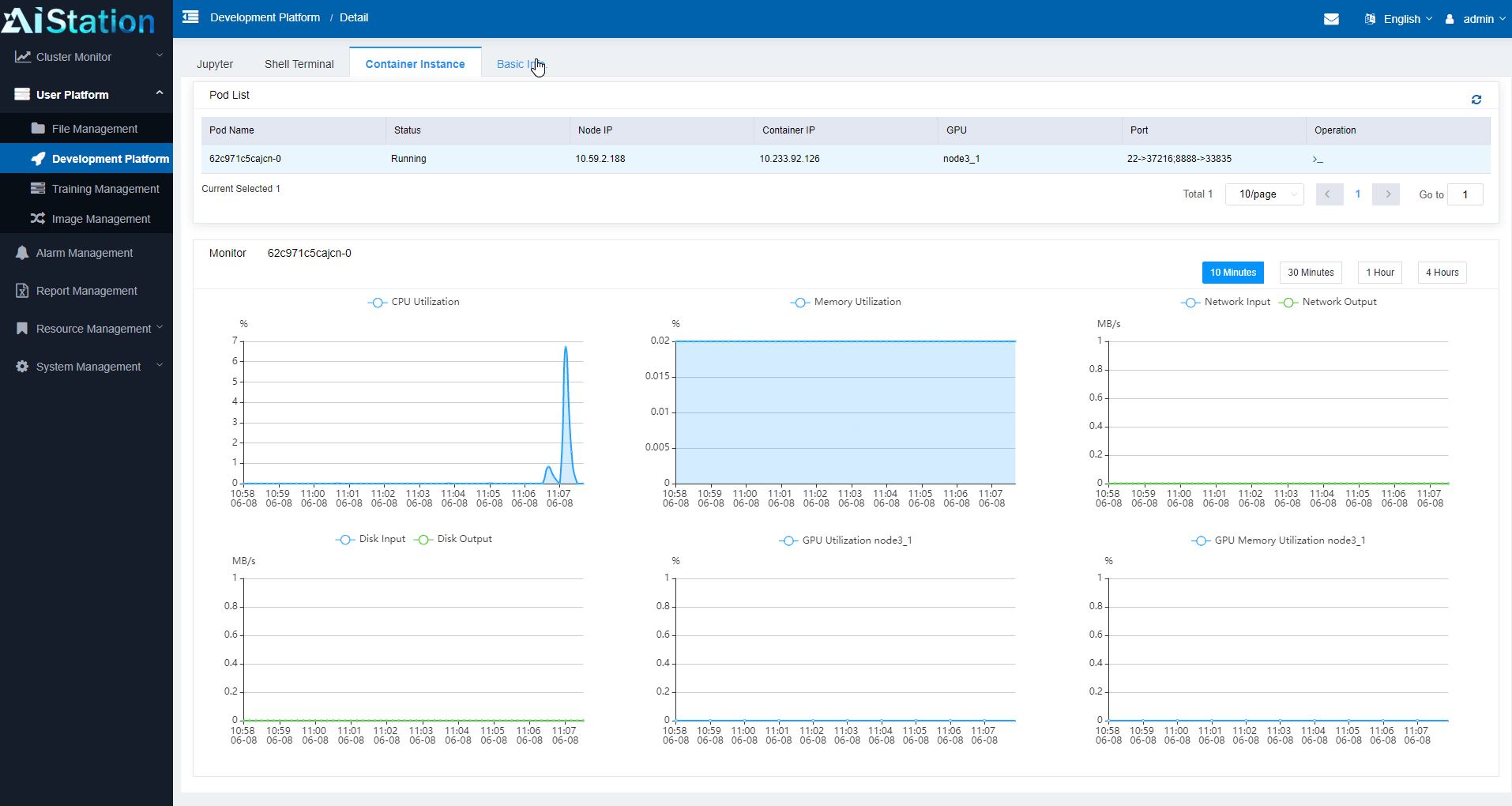
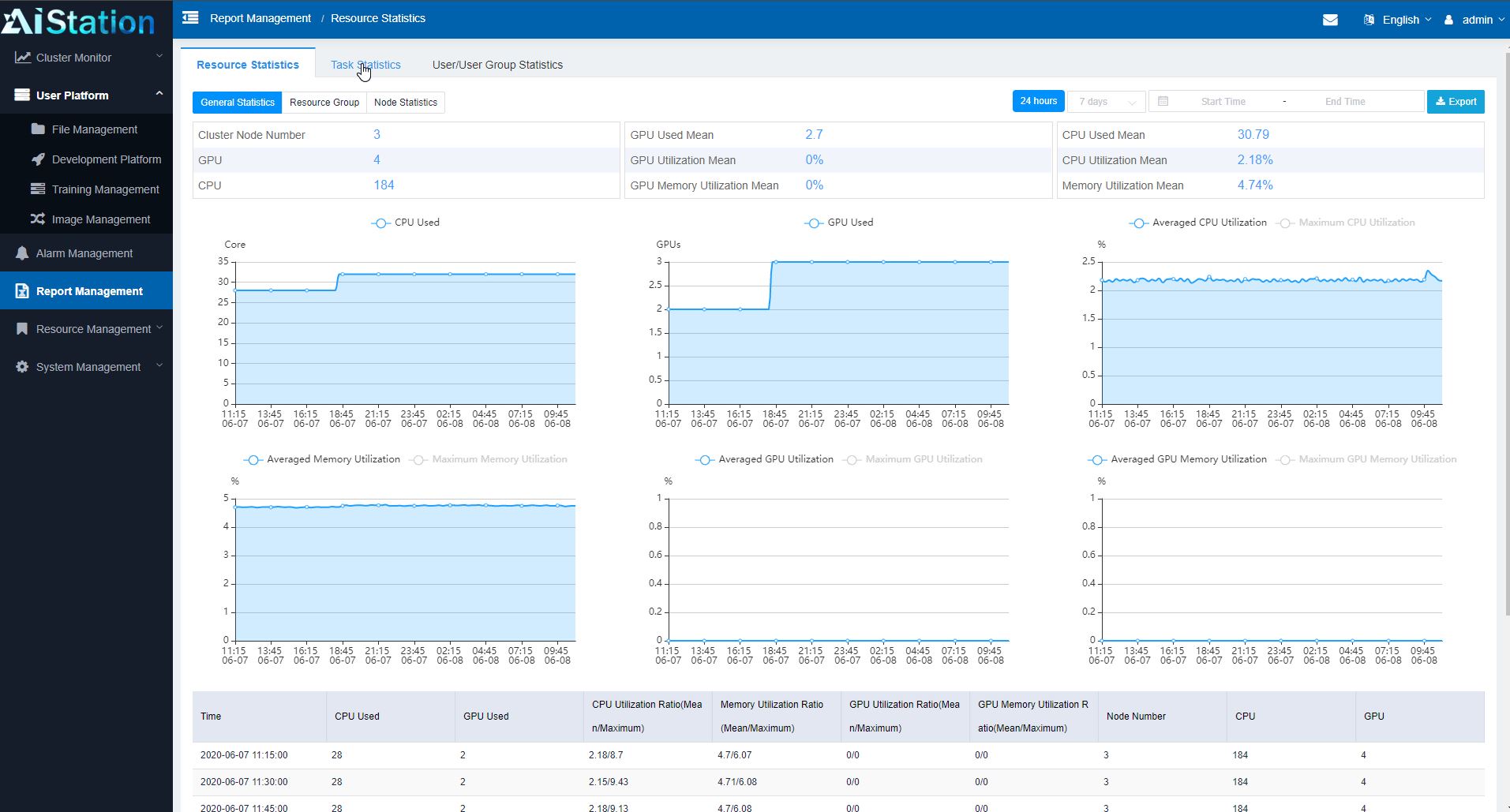
AIStation also has a fairly comprehensive dashboard system for monitoring clusters. One can see, for example, the utilization of CPUs, GPUs, and memory. In terms of cluster lifecycle management, this type of data collection helps administrators see how well they are provisioning resources and how much capacity is in the system. For example, if a cluster is running at 50% CPU, 60% GPU, but 95% memory, it is a good indication that next-generation nodes need more memory capacity.
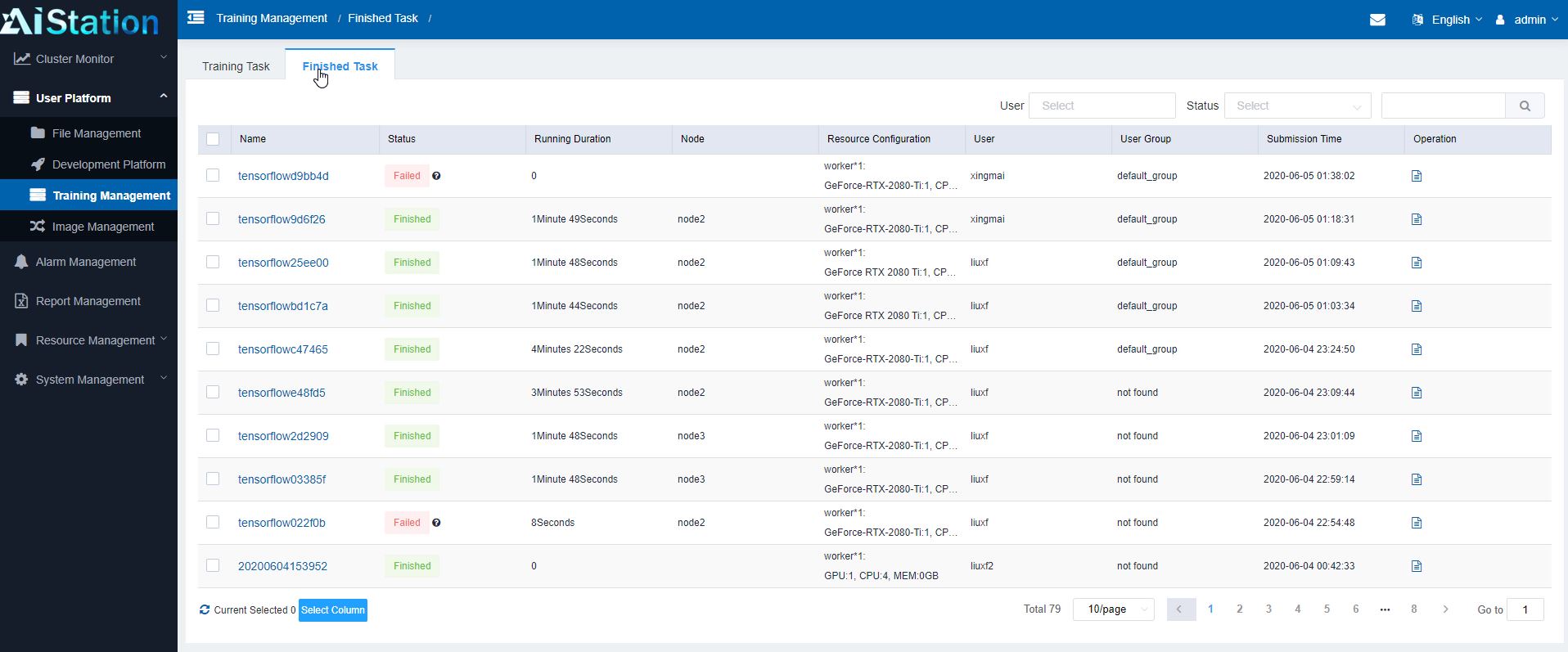
Admin users can also see finished tasks to see what users have run previously, including whether the jobs were successful. There have been cases where people will, for example, mine cryptocurrencies on company GPU clusters. A feature like this provides the audit trail in terms of what has been run which is an important function.
Aside from the above functionality, another important aspect is managing what resources users have in the system they are working in. I thought that is better to cover from the perspective of a user in the system.
Hands-on with Inspur AIStation: User View
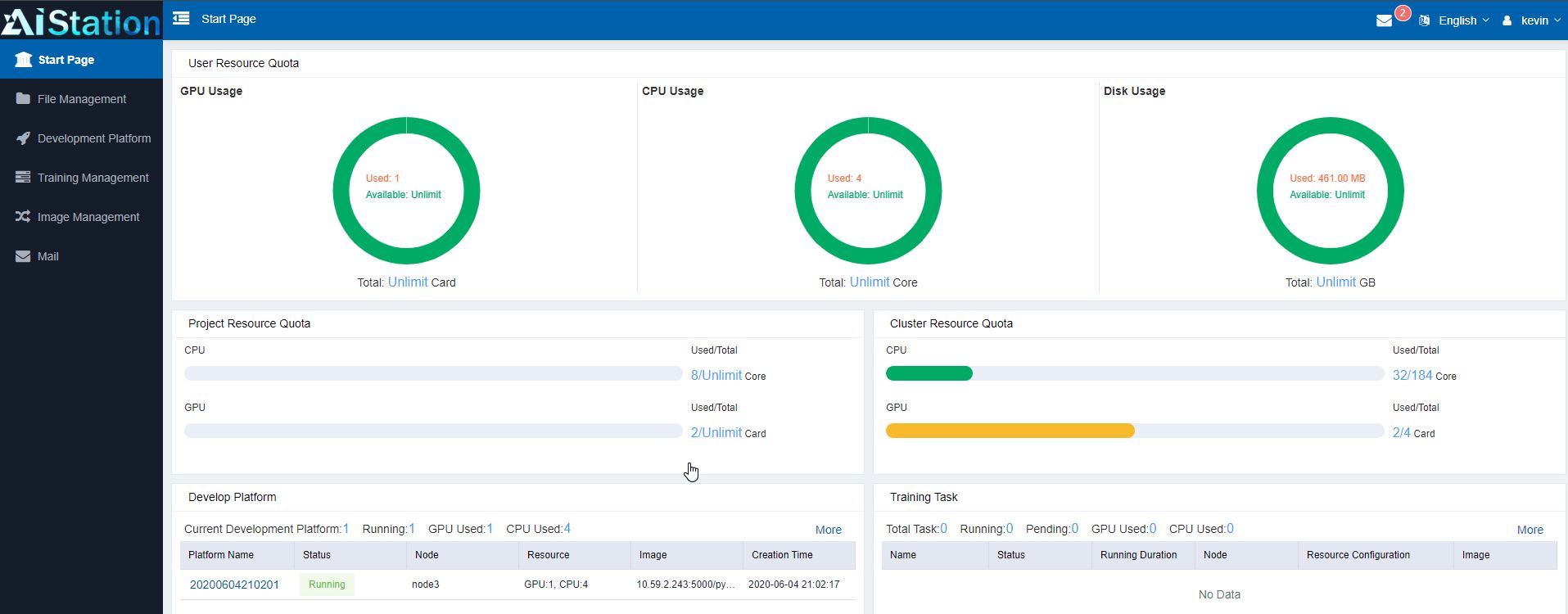
Each user is given access to a set of resources. As they log into AIStation, they can see their dashboard. Many of these usage limits are defined via user, group, and resource group features shown in the administrative section. This is the view for the user:
If, for example, a developer wants to start a training task, they can look at the images available to train. These can be images from sources such as NVIDIA GPU Cloud or NGC or more standard images. AIStation also has the ability to have group or even user images so one can select those container images more easily. One can also see private and public views, administrators can define images as private or public which can be important for sensitive images that need to be limited to specific groups or employees.
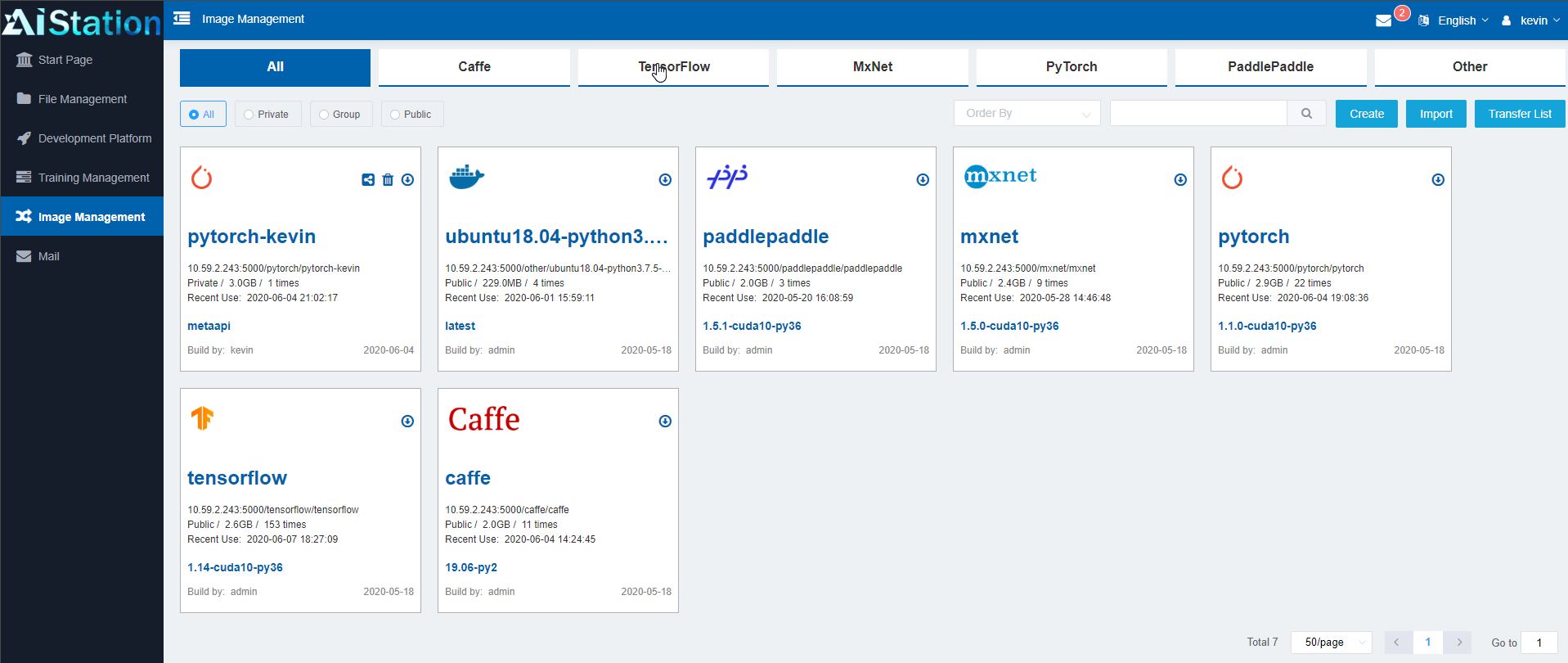
These images are important because as one creates tasks in the system, these are the images they may be using. Inspur does not support just one framework here. Instead, a user can use tensorflow, pytorch, paddlepaddle, or others all managed through the central repository.
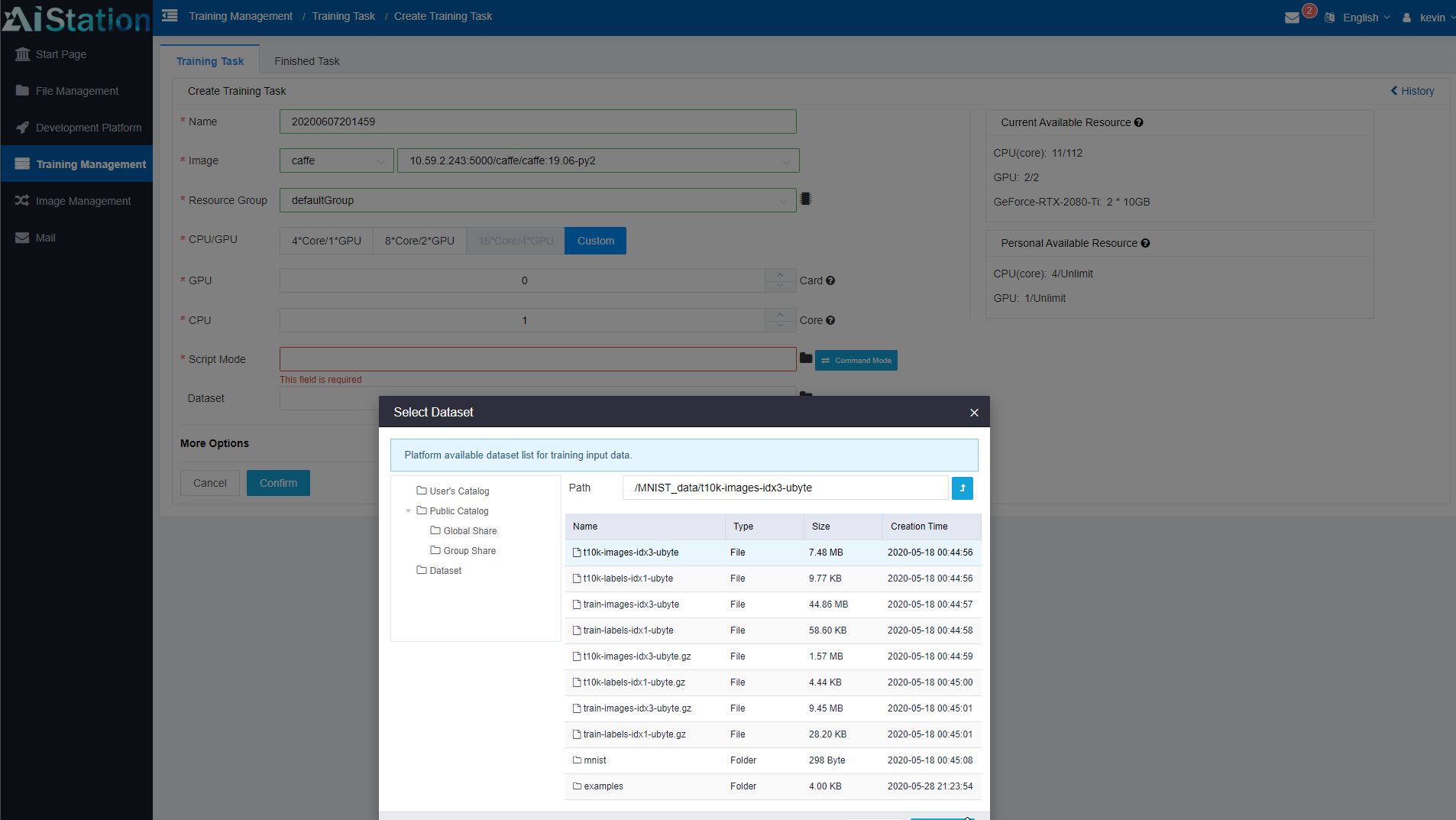
Since data management is extremely important in AI clusters, AIStation has the ability to define and store data sets. Admins can also set permissions on those data sets. This is important since there are data sets that only certain users should be able to see. From a user perspective, they can see which data sets are available for their use. That gives a user the ability to tie container images, to nodes/ physical resources, and the data that will be used in training.
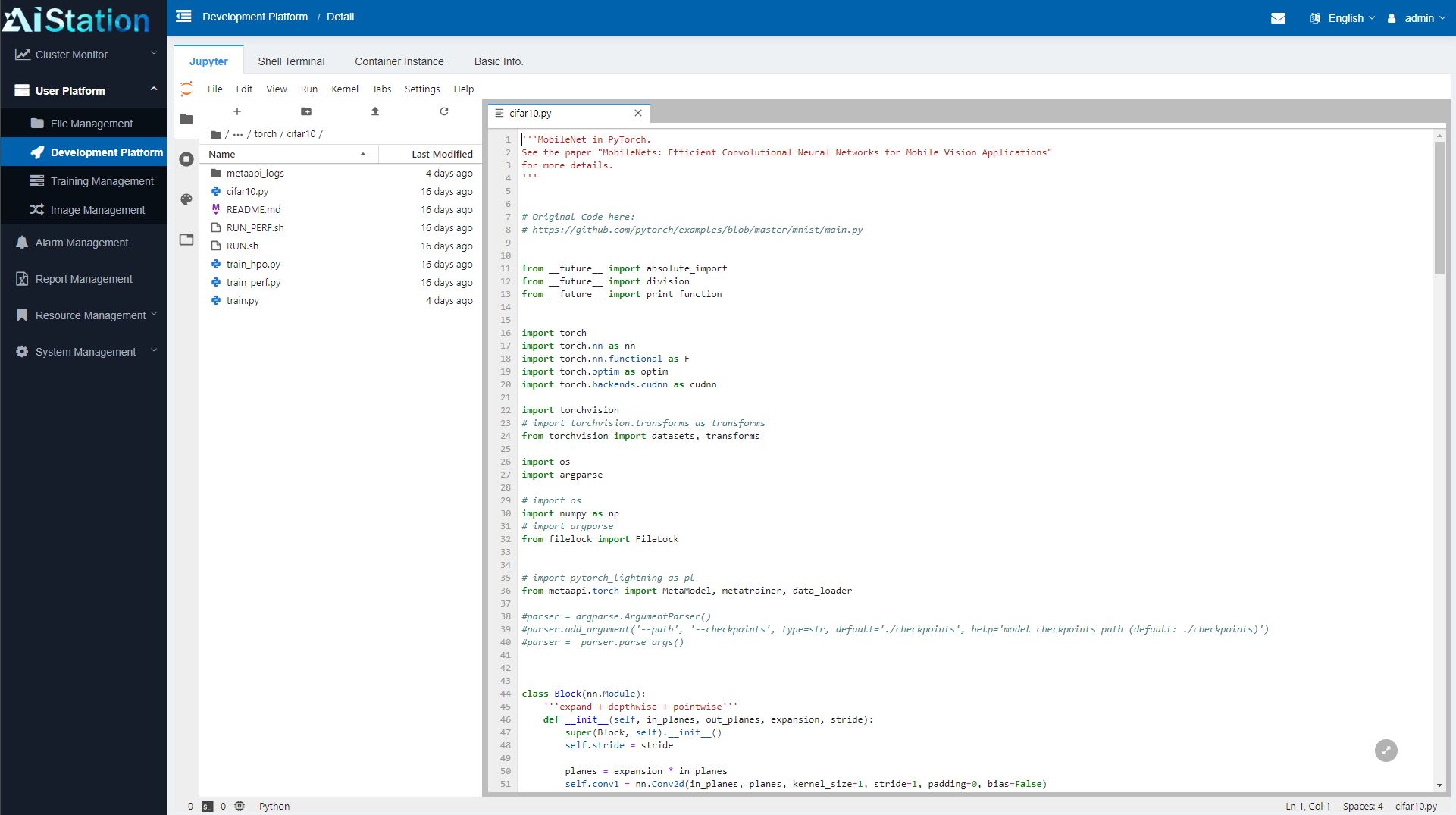
Within AIStation, one can also do work such as loading a Jupyter notebook and editing python files directly. The notebooks can then be saved on the storage back-end for the cluster and shared with other users easily.
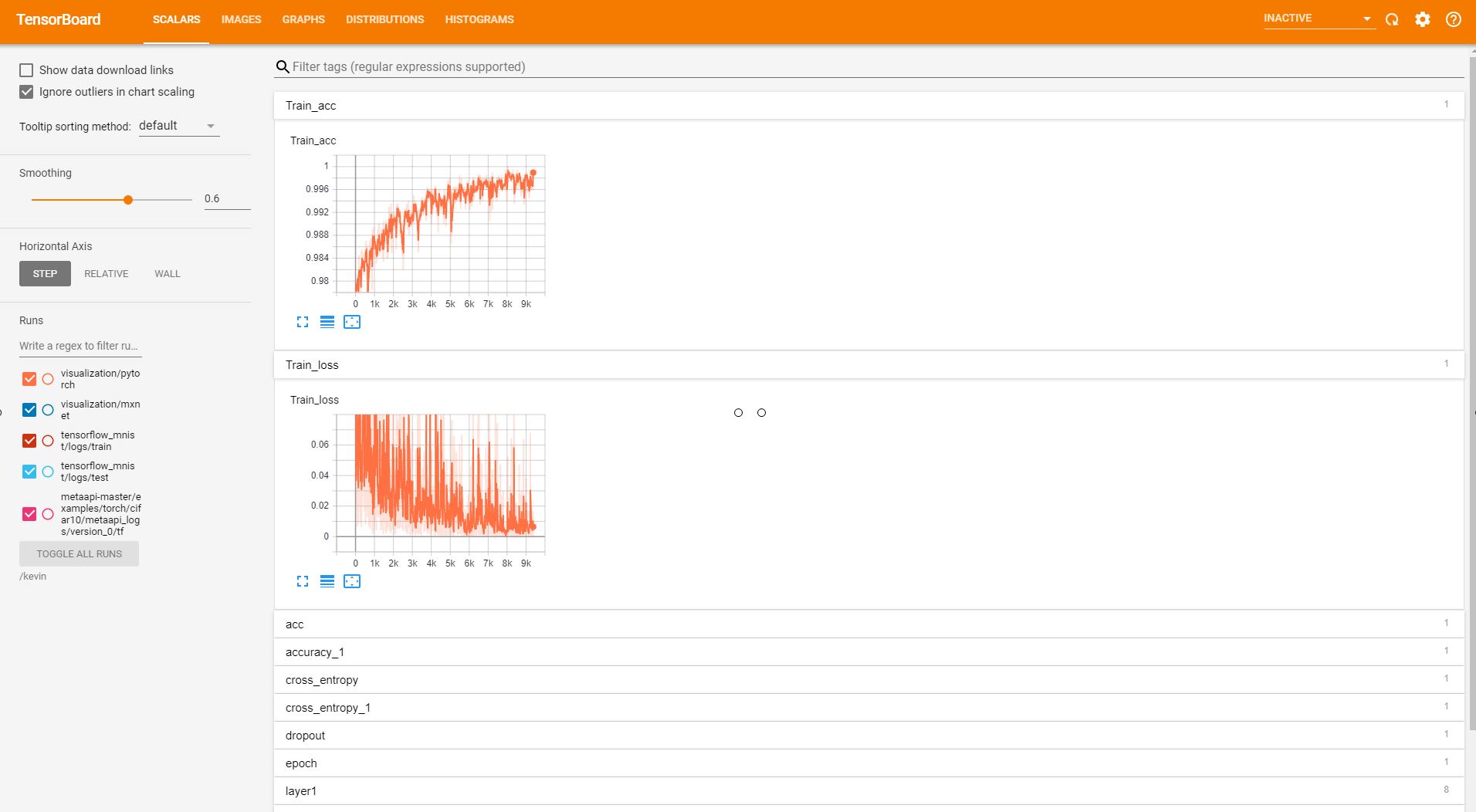
Once tasks are launched, the AIStation platform integrates a number of visualization tools. For example, one can launch Tensorboard (shown) or even tools such as Visdom or Netscope to provide visualization from a drop-down menu.
We did not screenshot this, but there is a lot more functionality available here. For example, one can click and get into the container’s terminal directly from the web GUI.
Since training jobs can take many hours or days, one can see the status of their jobs and check the results along with pending jobs and their history.
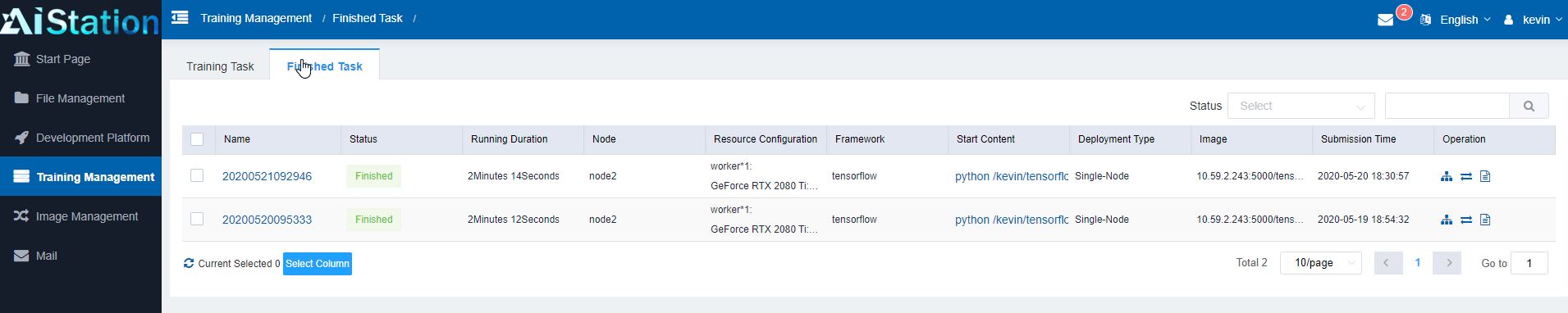
As one can tell, this is a solution meant to handle many users for a company along with many nodes even with multiple generations of GPUs. There are a few other features we are not showing here such as e-mail alerts and notifications for admins and users, but this is clearly a solution that is designed to run a company’s entire AI operation. As such, I wanted to ask a bit more about the business side of AIStation to get into its go-to-market strategy.
Follow-up Q & A with Liu Jun of Inspur
For answering the go-to-market strategy side, I was able to ask Liu Jun head of Inspur’s AI and HPC business a few questions. If that name sounds familiar, that is because he has helped STH before, such as in our Interview with Liu Jun, AVP, and GM of AI and HPC for Inspur.
Here is a bit around the go-to-market strategy of AIStation from our Q&A.
Patrick Kennedy: How does Inspur plan to go-to-market with AIStation?
Liu Jun: AIStation is sold both through direct sale and channel sale; We have dozens of channel partners globally to sell AIStation.
PK: Can AIStation integrate cluster nodes from other server vendors?
LJ: Yes, AIStation is capable of integrating cluster nodes of other vendors.
PK: What are the target customer segments and sizes? Are there particular industries that AIStation is being sold into?
LJ: Since its launch in April 2019, AIStation has exceeded $7 million in sales just in one year, and has actually applied in industries such as finance, education, Internet, and smart cities.
PK: Is this designed only for large organizations, service providers, or will it be sold into smaller organizations such as startups?
LJ: AIStation is designed for the field of deep learning development, large and small enterprises covering industries of finance, Internet, communications, transportation, medical, education, etc.
PK: What is the licensing model?
LJ: It is sold per GPU server node.
PK: Is upgrading the license done by purchasing a new key or will the customer’s existing key get new entitlements from Inspur’s registration servers? (As a quick background for our readers, we did not show this above, but there is a license key page on the web GUI)
LJ: Users acquire a free AIStation upgrade service in three years and need to purchase a new key after that to upgrade.
PK: What are other future services that Inspur plans to offer with this solution?
LJ: In the future, AIStation will support more AI accelerators and achieve heterogeneous acceleration of resource management, scheduling, monitoring, optimization, etc. It will build up a more comprehensive AI development ecosystem and provide an integrated development platform for industry mainstream AI development tools, development frameworks, and deep learning models.
As always, thank you to Liu Jun for taking the time to answer some of these questions for our readers.
Final Words
The reason I wanted to show off both the AIStation hands-on view, along with the go-to-market is important. In the first year, AIStation has over $7M in sales for the software side. There are venture capitalists out there that would be thrilled to see an AI management software platform hit $7M in the first year for one of their portfolio companies. The point here is that although Inspur is releasing this as a product, it is really something that is already being deployed to paying customers today. These customers are already using this solution to manage their AI clusters and development teams.
If one takes a look at the current capabilities and looks to the concept of being able to use a heterogeneous mix of accelerators, one can quickly see where this solution is headed. What is different compared to some of the other cluster management solutions out there is that this is designed to be used even by larger organizations and it is all based on Kubernetes which is quickly becoming the primary tool for next-gen services.
Overall, this may not be something that you need if you are a small 2-3 person startup, however, as clusters grow in an organization, scheduling, and management become a larger task. Inspur is already providing the software that can scale to that challenge with AIStation.




