Computational storage is a small but growing segment of the market. To address this, the Samsung SmartSSD is being launched with a Xilinx Kintex FPGA inside to bring computational storage capabilities in a standard form factor. In this article, we are going to discuss how Xilinx and Samsung are delivering a computational storage platform.
Xilinx-Samsung SmartSSD Background
First, why computational storage. One of the big drivers is that moving data, at high speeds, across systems can use a lot of power and consumes bandwidth. With computational storage, data can be processed without bringing it back to the main CPU.
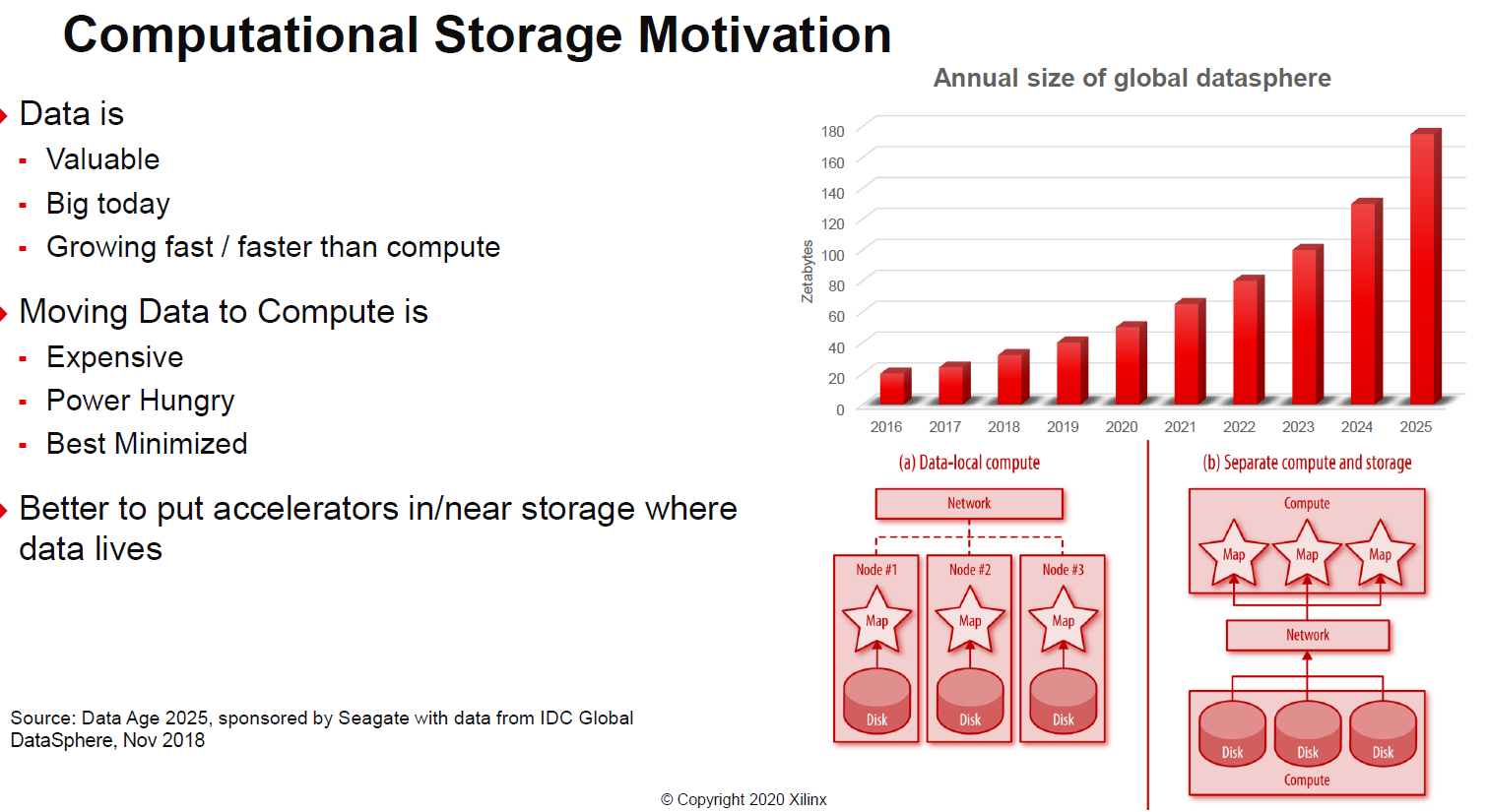
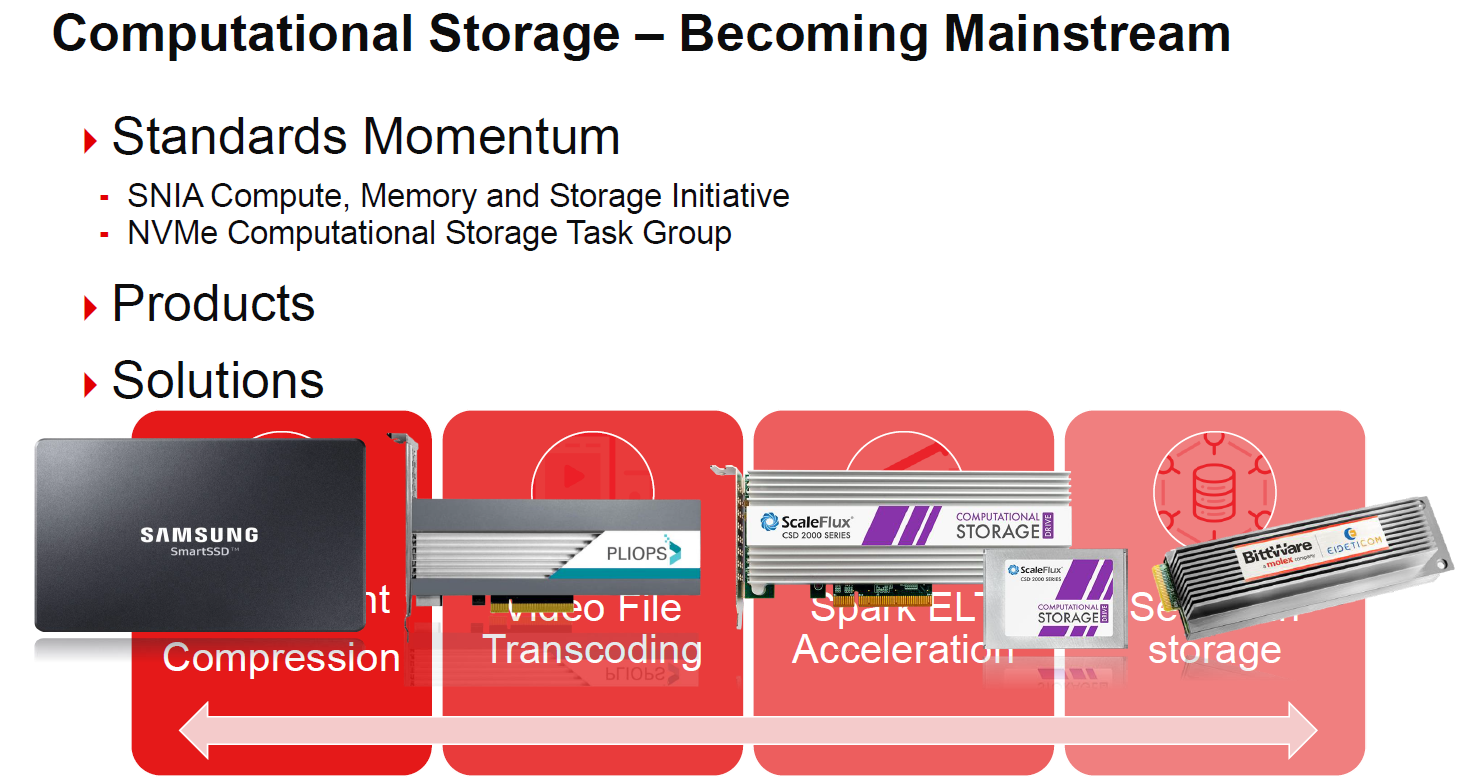
Part of the other driver here is that Xilinx sees computational storage as becoming mainstream, projected to be 5% of the market in only a few years. For its part, Xilinx is covering a number of different types of accelerators aside form the Samsung SmartSSD including those from Pliops, ScaleFlux, and BittWare.
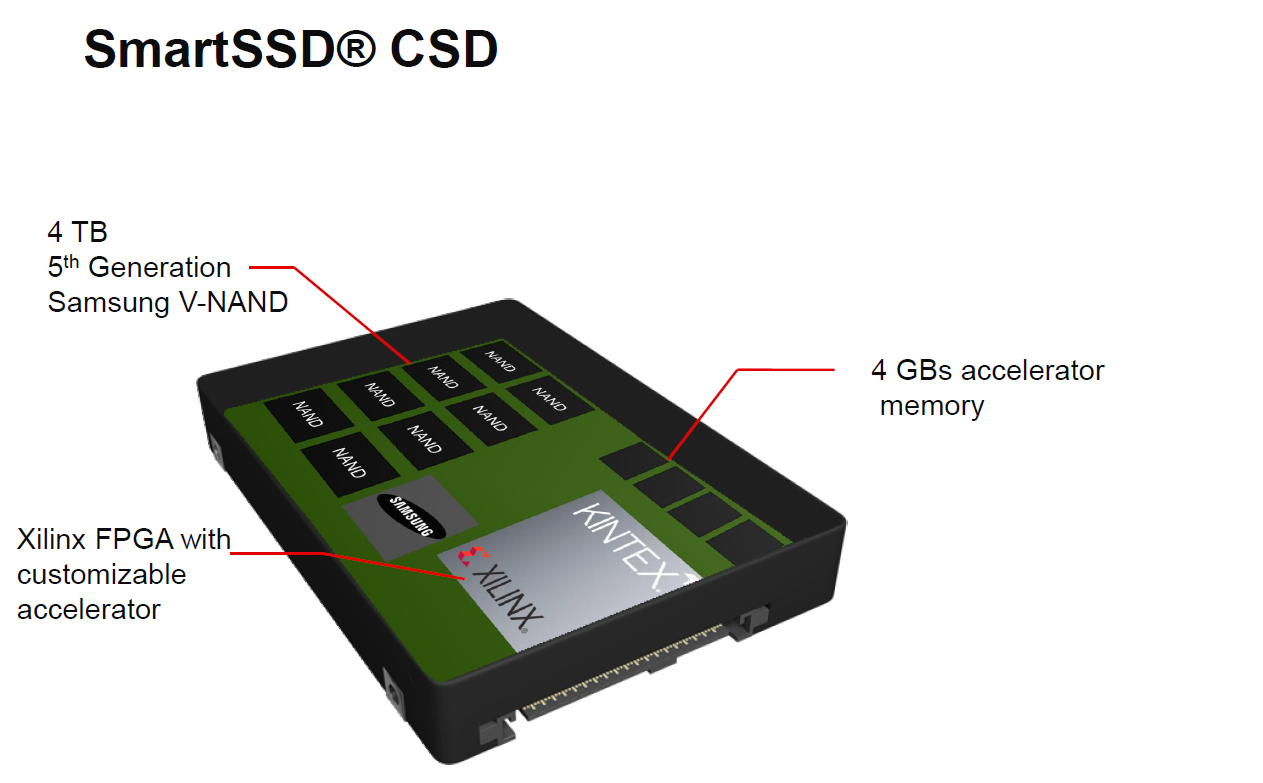
The basic Samsung SmartSSD has two main sets of components. One is basically a 4TB Samsung V-NAND SSD. This includes a NAND controller, and we are told DRAM for the controller to use as well. The second part of the solution is a Xilinx Kintex FPGA with its own 4GB of memory.
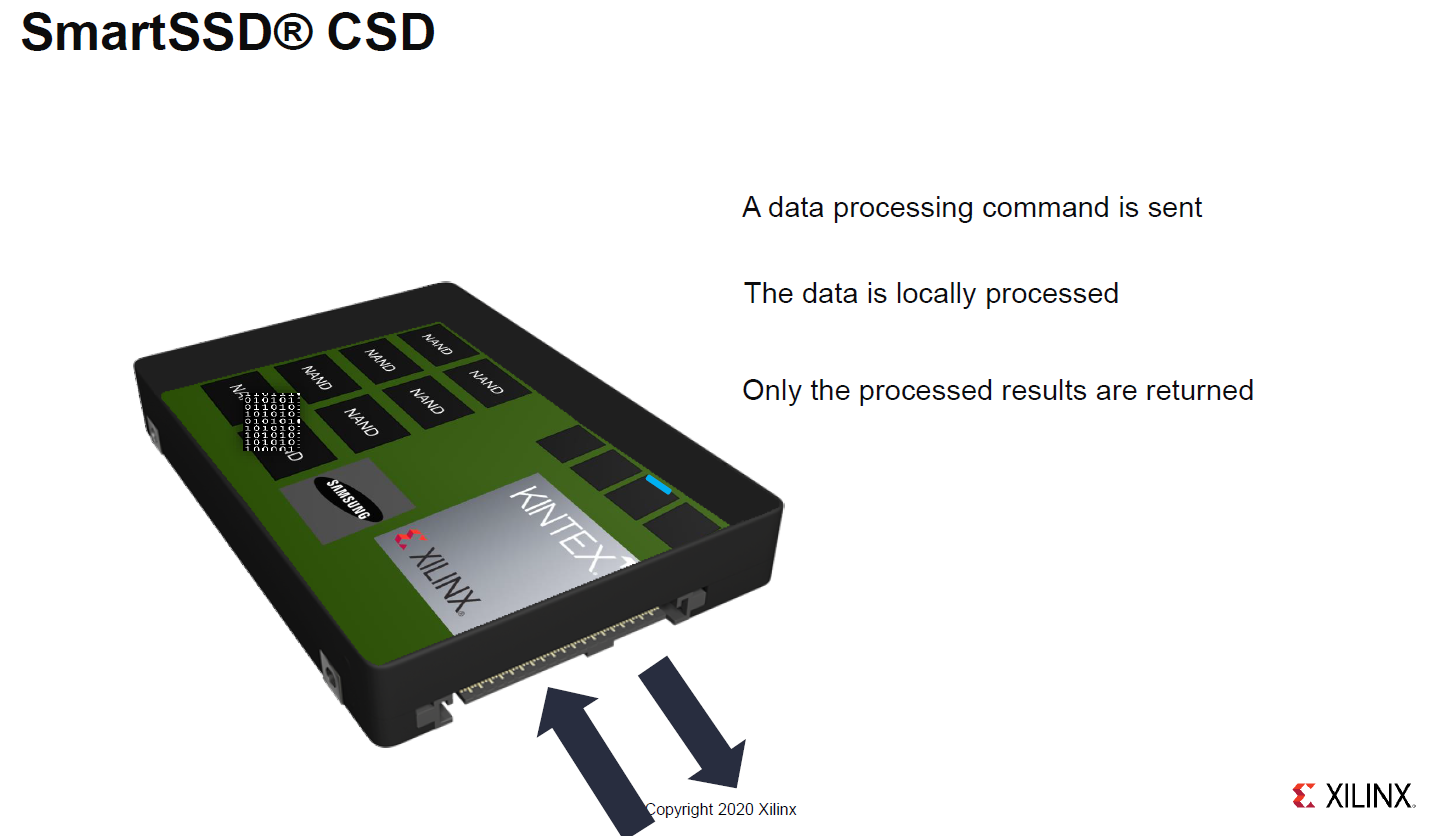
The basic flow is that commands can be issued to either the SSD or the FPGA portion of the drive and processing can occur at the FPGA instead of going back to the host system.
We are going to show an example later but a common question will be how are these programmed. One can use a standard storage stack or the OpenCL stack for computational storage aspects.
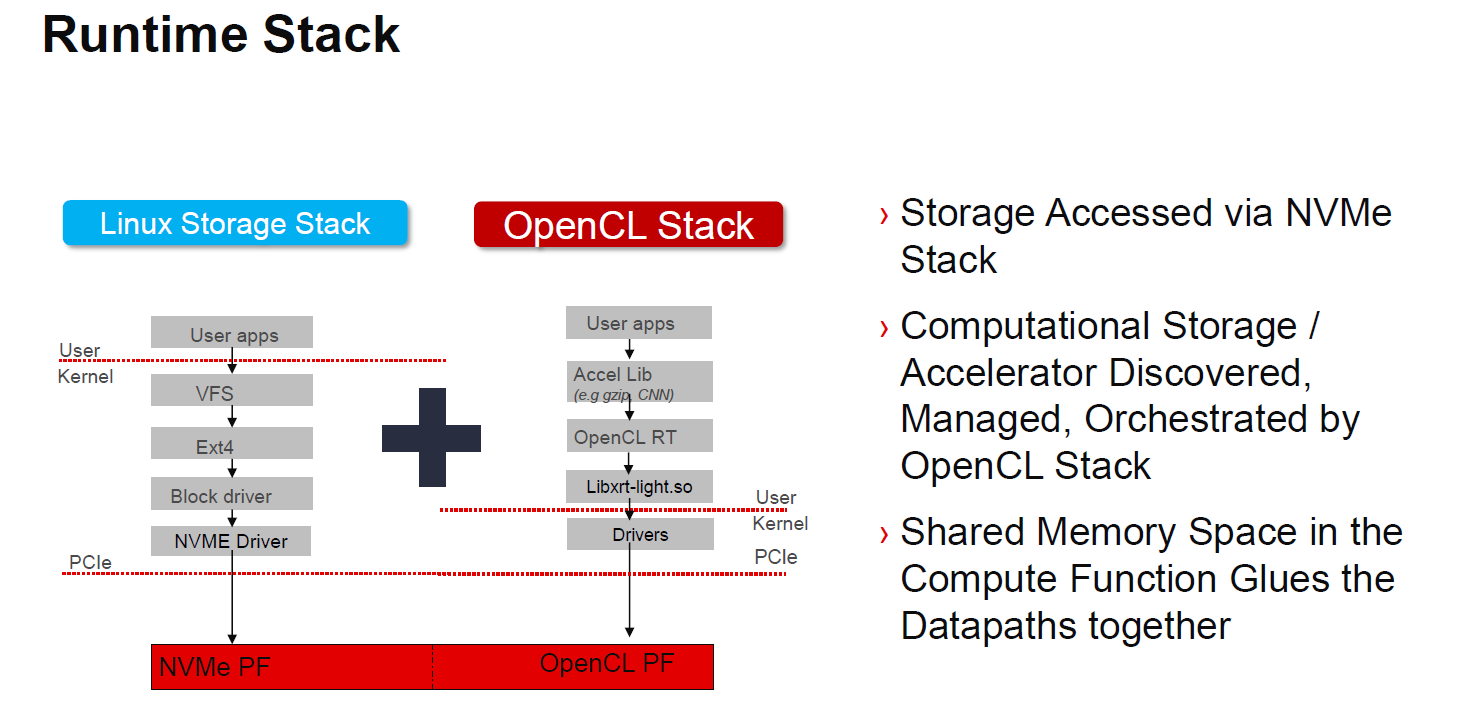
As one would expect with a FPGA, there is a tie in with partner IP solutions as well as those that Xilinx and Samsung will have.
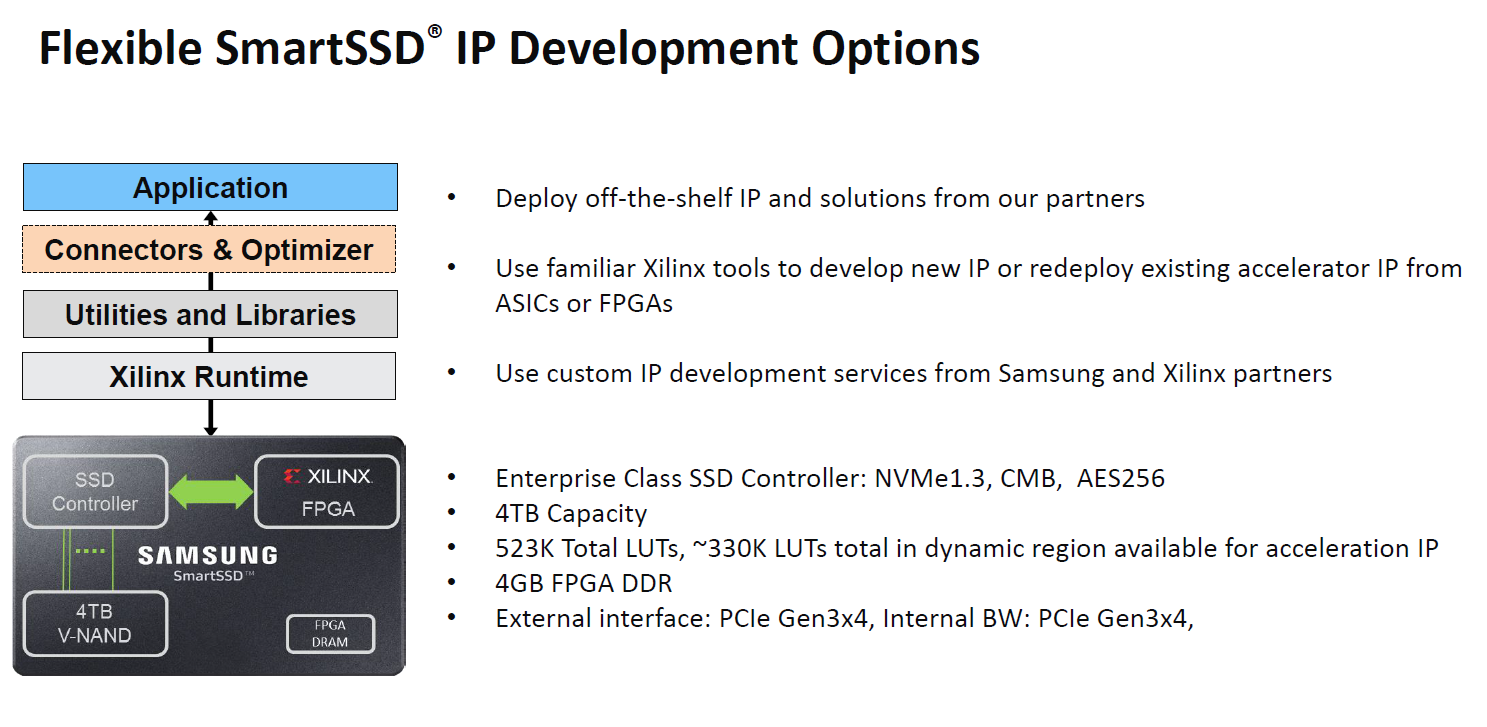
The Xilinx Storage Services (XSS) are offloads available for the platform. These include compression and crypto offloads.

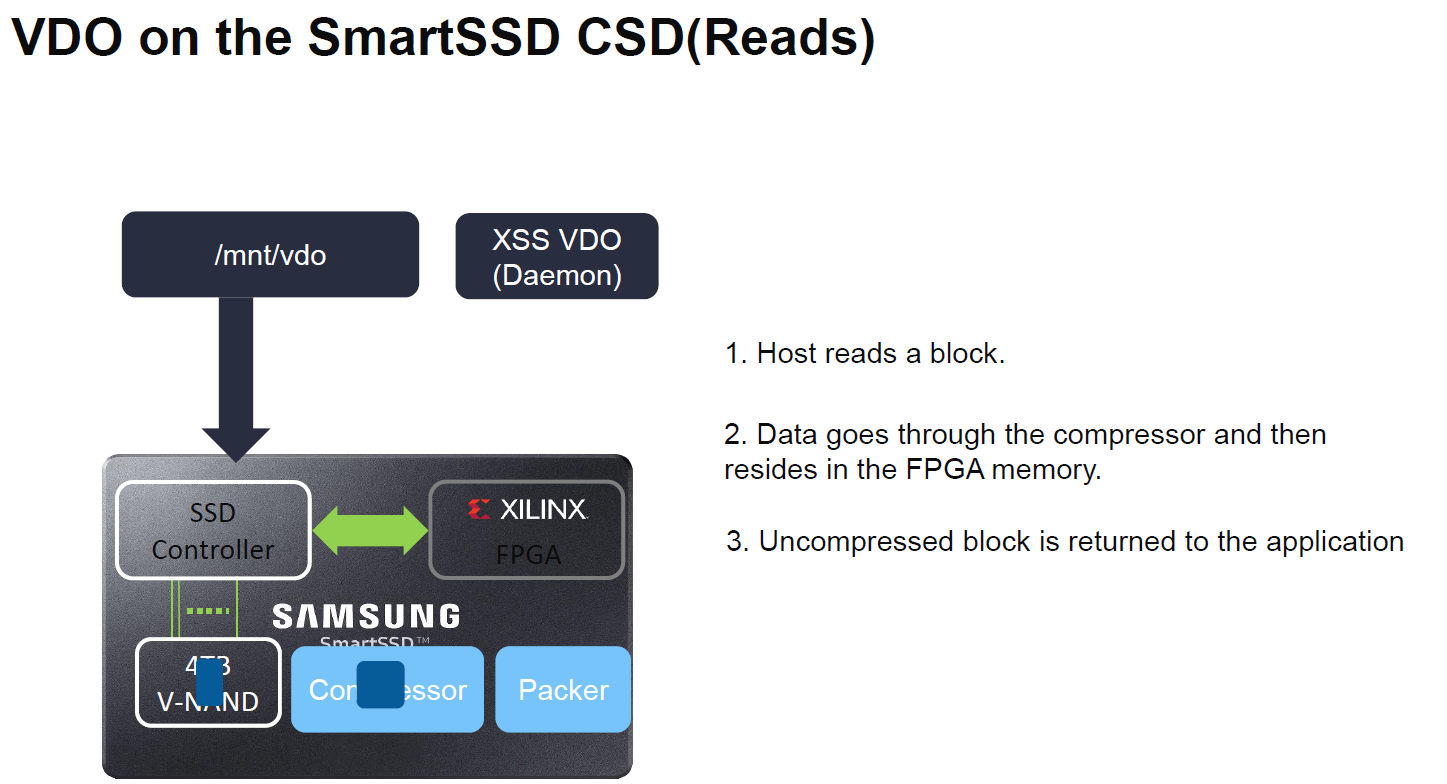
Taking the compression in VDO as an example, the following slides have the basic flow:
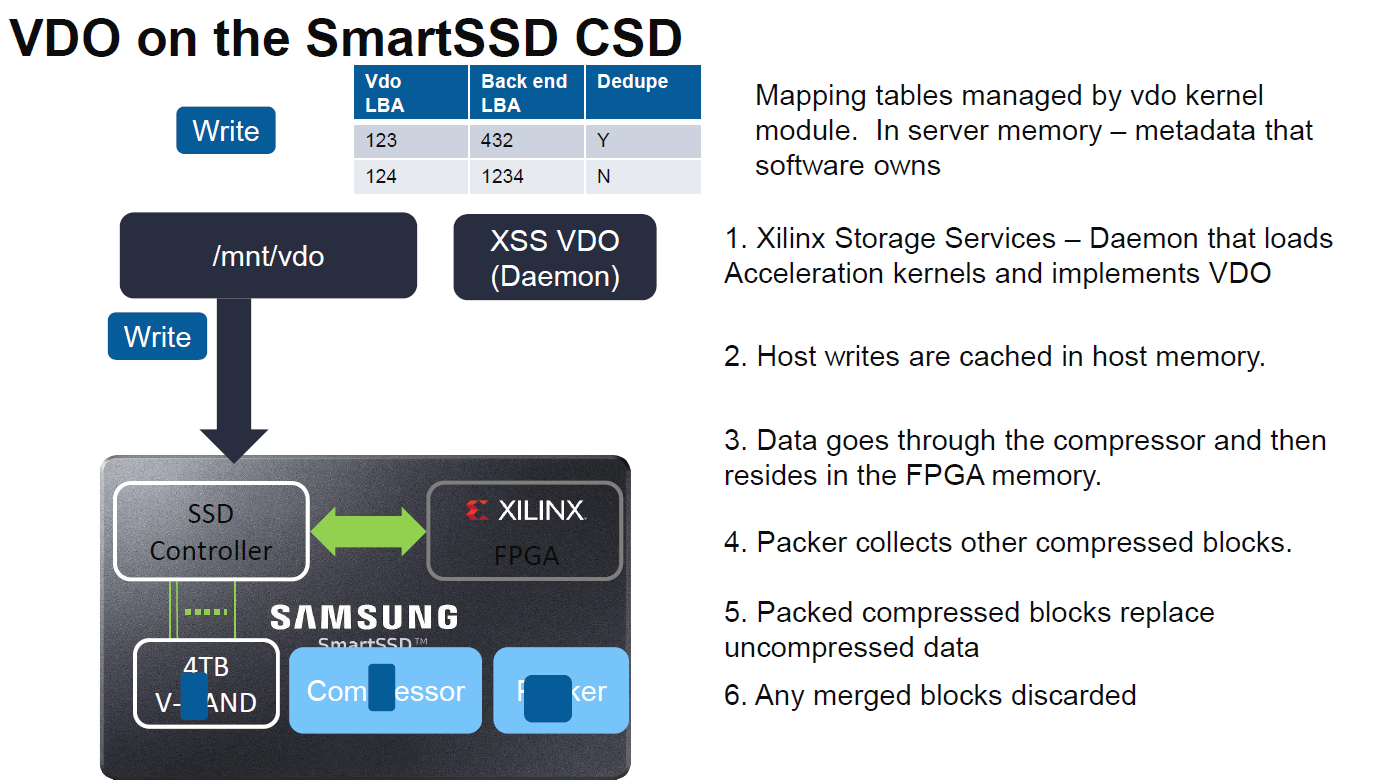
For reads, the FPGA is used to decompress data at the SmartSSD. By putting the compression on the SSD, Xilinx says it can get better compression ratios.
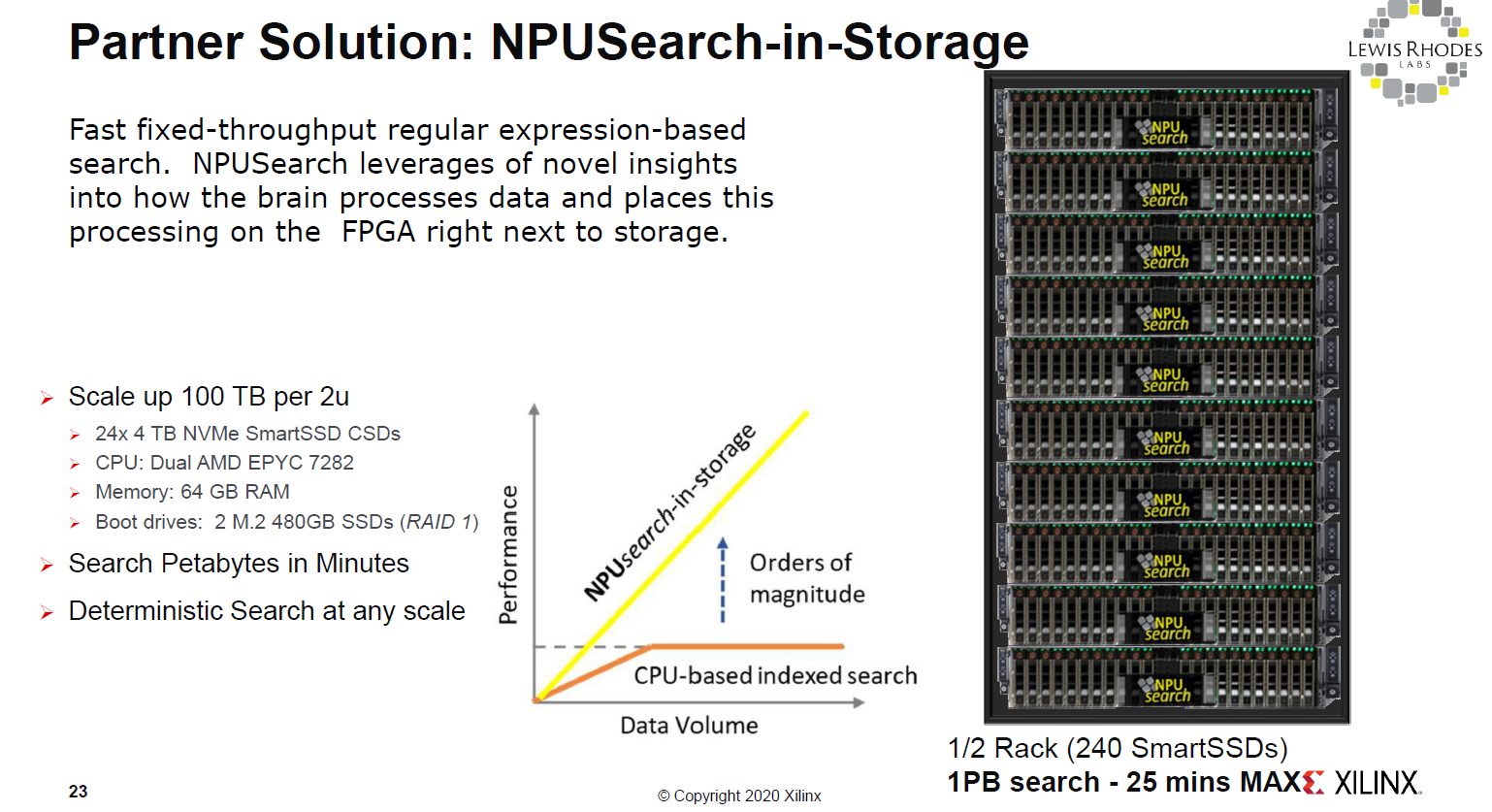
In terms of examples, we wanted to highlight one from Lewis Rhodes Labs where they are doing NPUSearch using computational storage. Effectively here the SmartSSDs are being used to scale out the number of accelerators with the number of SSDs. An application can send requests to the storage, data can be evaluated at the drives, and only results passed back to the main system.
Since many of our readers will have noticed this, we asked about the PCIe Gen3 and we were told that there is a roadmap to the future.
Final Words
For STH readers, an immediate question is going to be why computational storage? Part of this model is that accelerators are tied to storage. For accelerator companies, this is great. Many of our readers though are going to ask about why not use DPUs instead. If you missed it What is a DPU A Data Processing Unit Quick Primer is a good resource there. We asked since if the only goal is offload, and the SmartSSD is in many ways two devices that are co-packaged, then it could make sense to offload to a bigger chip. We were told that it is less expensive to use a smaller accelerator on each drive than to scale to a larger accelerator. This is one area that we know there is a lot of momentum behind each model in the data center. It will be interesting to see which ultimately wins.





How is data redundancy covered on these drives? Can the accelerators work if these drives are used on a zfs setup?