Windows Storage Spaces is a great software-defined solution that has been part of the Microsoft stack since Window Server 2012. It provides enterprise storage features such as tiering storage (SSD with Hard Drive) and a resilient file system such as ReFS. It is a very powerful solution combined with SMB 3 and RDMA which deliver great performance even when compared to other software-defined storage solutions. One of the major complaints against the Windows Server 2012 iteration was complicated hardware replacement procedures which require PowerShell functions. These procedures can be an issue with complex arrays and admin who are not familiar with PowerShell. Windows Server 2016 Storage Spaces addressed some of the complex issues and simplified the procedures. Today we are going to cover how to replace a failed hard drive in Windows Server 2016 Storage Spaces.
How to Replace a Failed Hard Drive in Windows Server 2016 Storage Spaces
The following procedure was based on Windows Server 2016 DataCenter Edition Build 1607 to demonstrate how to replace a failed hard drive. The procedure is not as straightforward as some other software-defined storage solutions, so we wanted to show the procedure.
From Windows Event Viewer, there are system logs indicate bad block from hard drive.
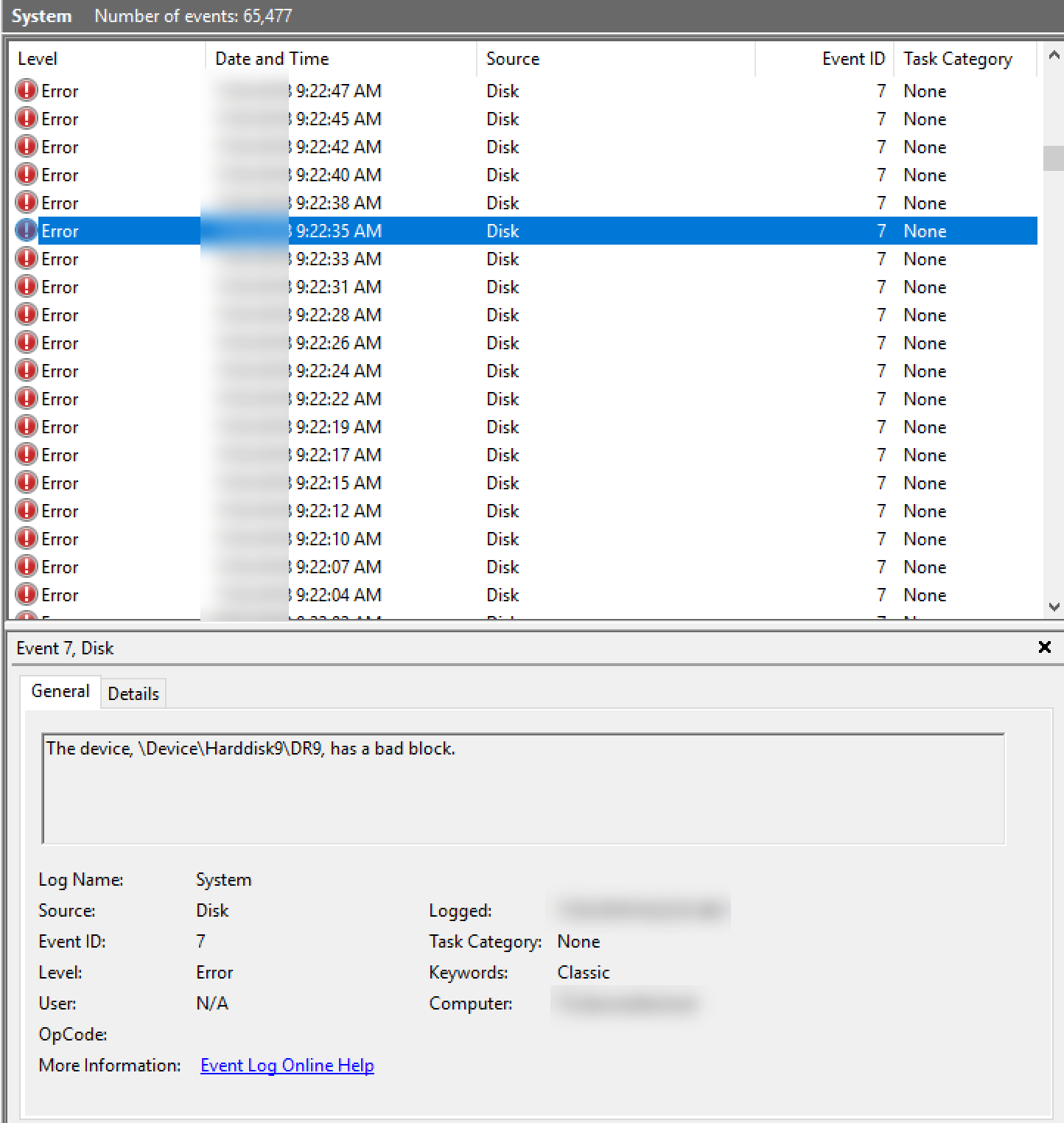
In order to find out the actual hard drive info, we need to run the following command to identify the hard drive from the server:
Get-PhysicalDisk | select deviceid,friendlyname,serialnumber,size,physicallocation | sort -Property deviceid

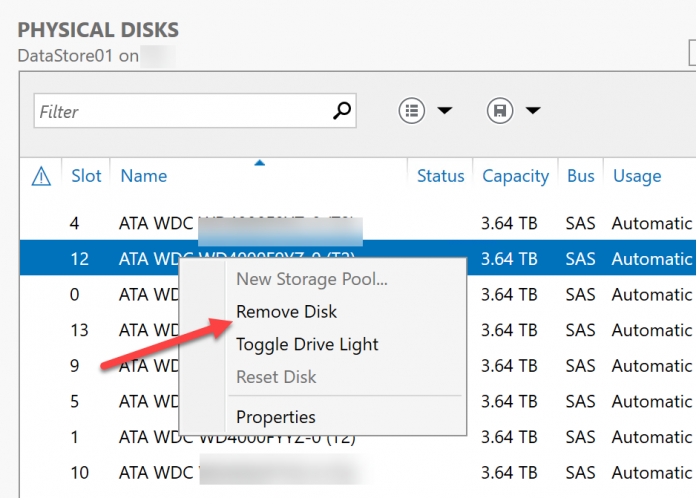
From this output, we can identify the failed drive 9 is in slot 12. Note, this is working on a SATA hard drive sitting on a SAS infrastructure.
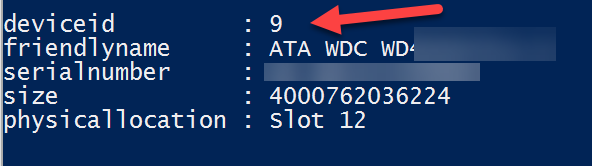
We need to locate the physical drive. The easiest way is to go to Server Manager, Storage Pool, Physical Disk then select the hard drive in slot 12. Choose Toggle Drive Light (if your system supports this feature):
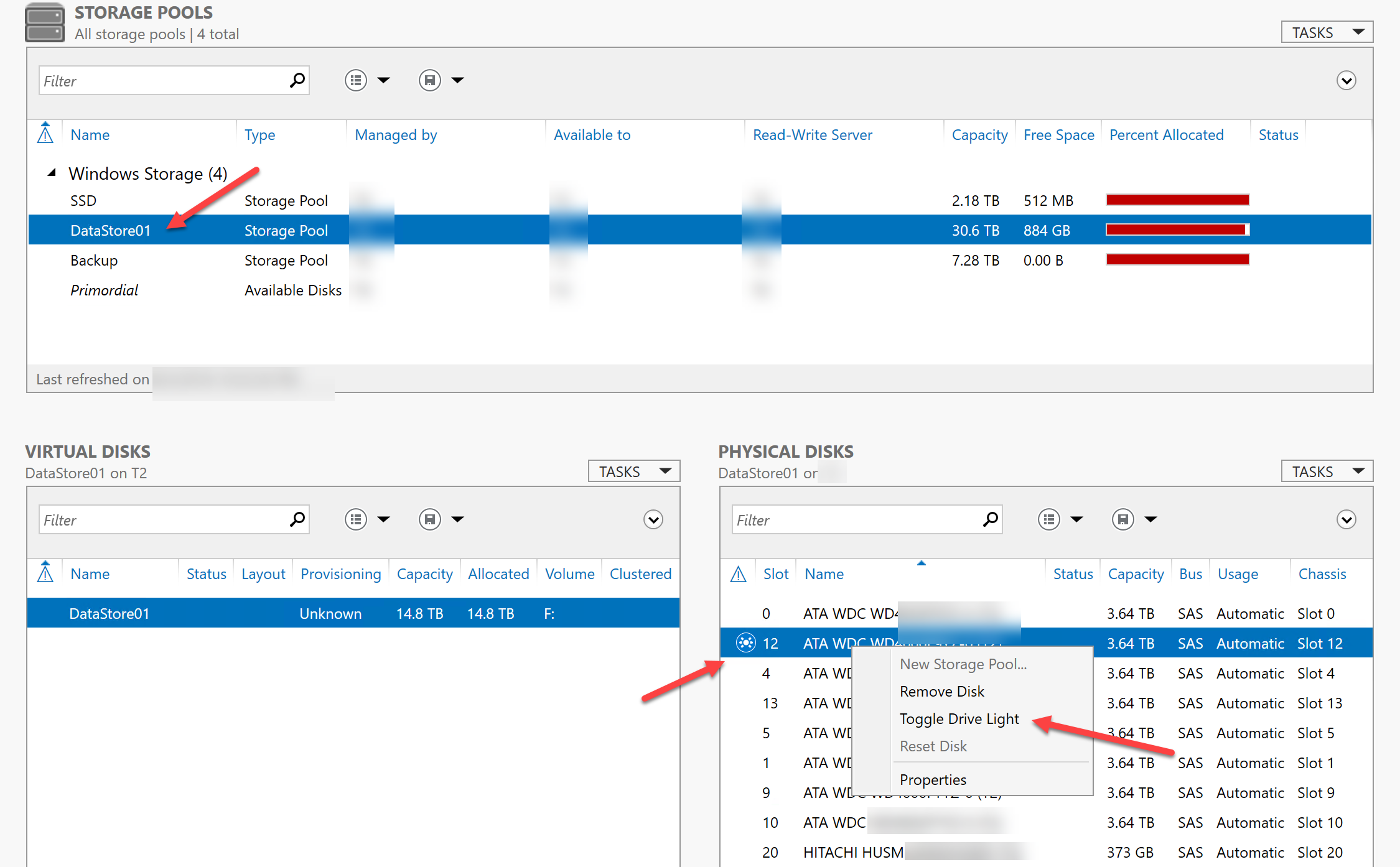
Before we remove the drive, we need to place the same size hard drive in the system, join to the pool and set to automatic mode. If you fail to do this, as many do during their first replacements, you will get the following warning.
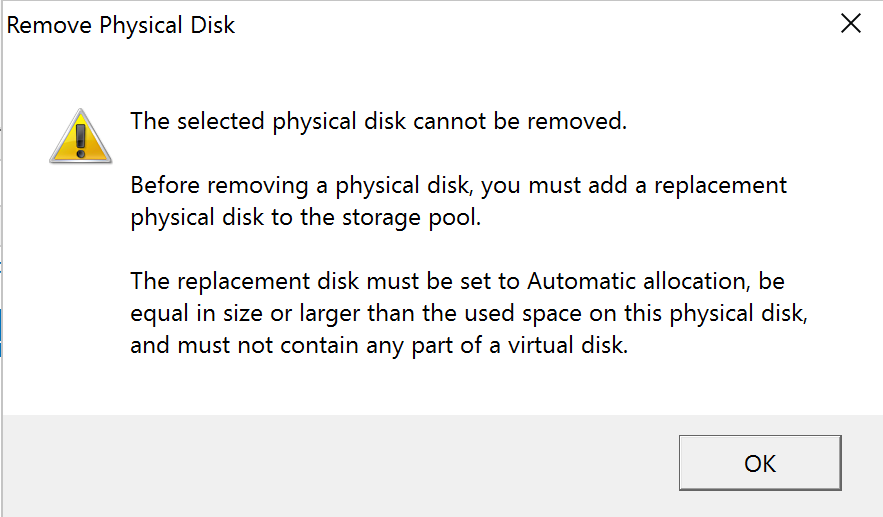
Instead, you need to add the new hard drive to the system. Then you will need to rescan storage:
Once this is done, you can add the new hard drive to the Storage Pool.
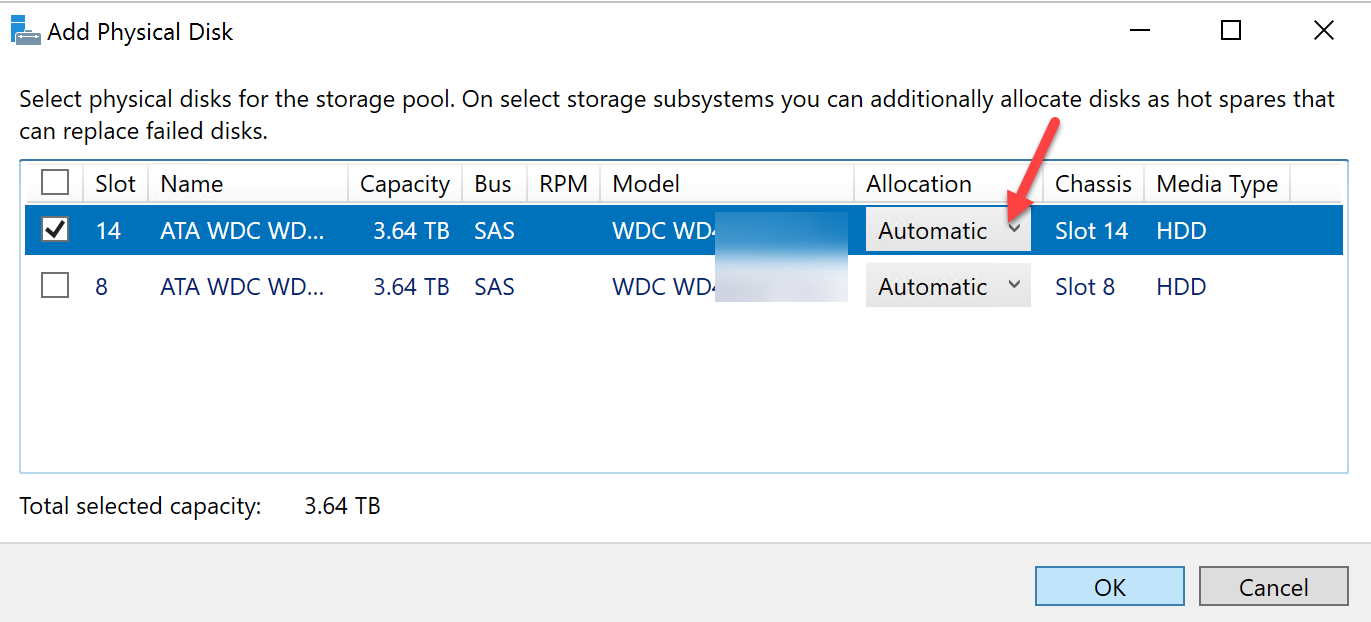
You will want to add the drive as Automatic for allocation.
After the new drive is in the Storage Pool, then remove failed hard drive.
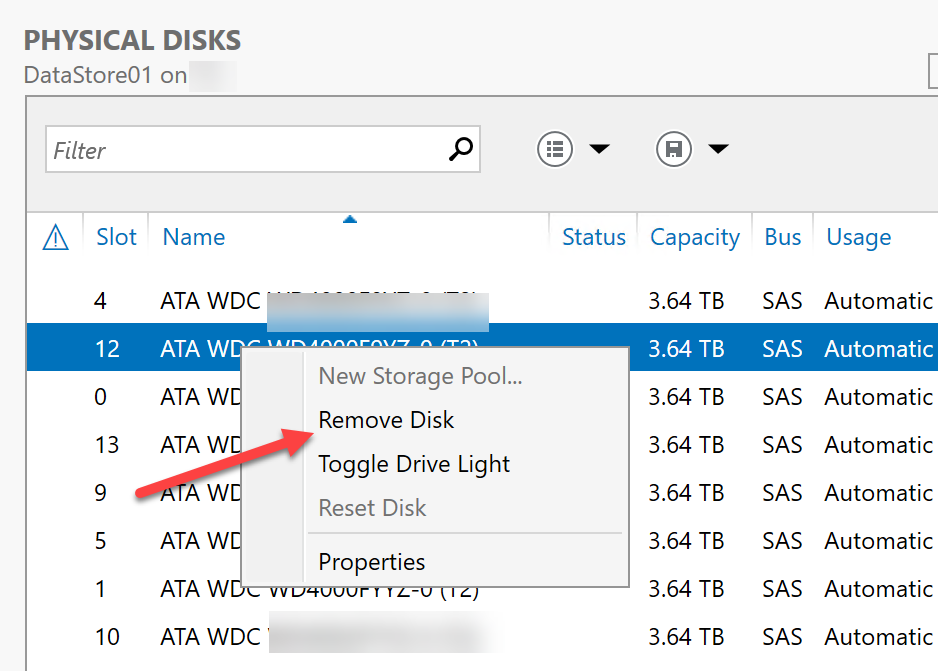

Do not make any changes to the Storage Pool while repair operation is going on.
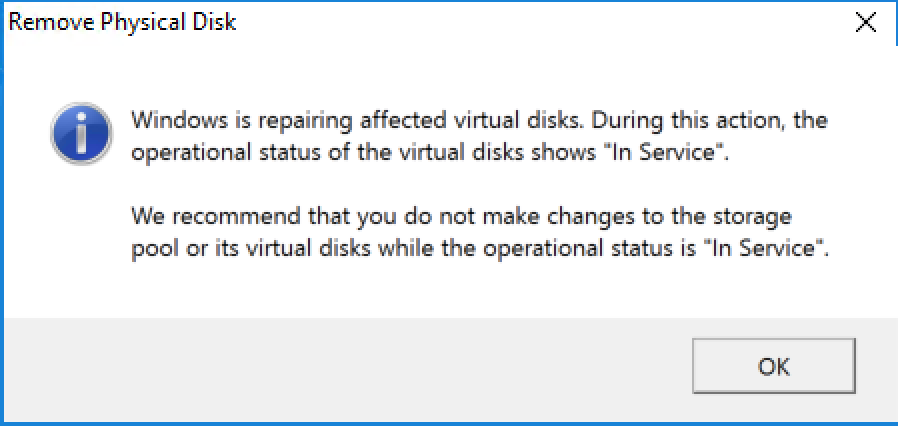
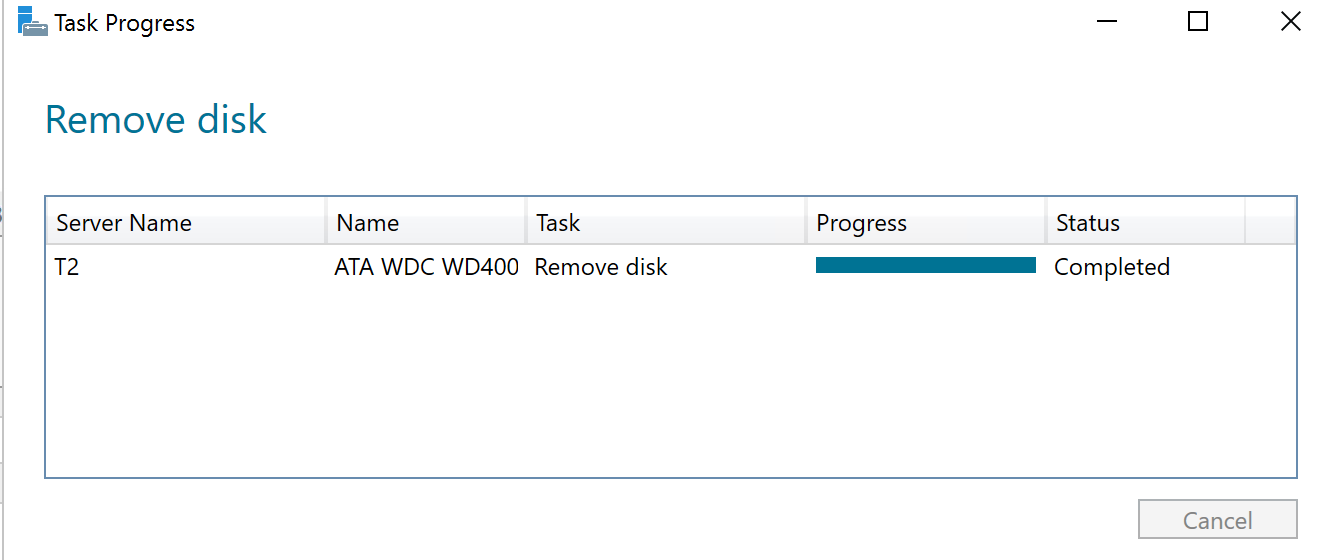
After some time, the old hard drive will be removed from the pool and the new drive will be assimilated. For the PowerShell fans, you can use get-storagejob to follow the progress of the repair.
After the operation is completed you can safely remove the failed hard drive.
Final Words
From the procedure above you can see the Microsoft made replace failed hard drive very easy in Windows Server 2016. People with minimum PowerShell knowledge should be able to perform the task without any issues.
Software-defined storage has come a long way in the past couple of years. Hyper-converged storage has become mature with solutions like VMware vSAN, Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct, and Nutanix. We also see how those solution combined with “traditional” software-defined storage such as ZFS and Microsoft Storage Spaces could give the performance, flexibility and reliability to customers who prefer alternative flexible storage solutions from the traditional vendors such as Dell EMC, HPE, and NetApp.
We hope this guide helps a new Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Storage Spaces admin replace a failed hard drive. If you try removing the drive first and get the error shown above it can be an understandably frustrating experience.


“duplations”, huh???
Hmm. So this essentially requires a hot spare, or a free slot to be left in your system.
What happens if I remove the physical drive and install a replacement without selecting “remove disk”? What if I have a 24-bay server with all bays filled?
How about using NFS instead of SMB? It should be quite a bit faster. Can you guys do a perf comparison between the protocols?
Andrew:
Have the design with residency in software defined storage is a key element. For example, if the server has 24 bays, then I assume OS will take 2 of them (mirror) and you will have 22 bays available. If this is in a datacenter, then one or two spare drive will be highly recommended. (no different than standard RAID configuration)
Software defined storage does free us from traditional storage vendors but we need to follow some of the best practice.
Hopefully this helps.
Scott:
In the Windows environment, RDMA based SMB 3 has the best performance. NFS is not quite there yet. In a none Windows environment, it will be an interesting comparison. There is RDMA support for NFS, instead of SMB maybe block based iSER.
I’d typically want to run at least one hot spare, but lets try another tack – 8-bay 1U server, boot from internal SATADOM or similar. Two SSDs for cache tier, six spinners in RAID6 for capacity.
Let’s say I’m running three identical nodes with 3-way mirroring via S2D – sufficient cross-node hardware redundancy that I don’t really want to lose 25% of my capacity tier to a hot spare. With a hardware RAID setup, this isn’t an issue – if a drive fails, I pull the drive and slot in a new one. If Storage Spaces _requires_ that a new drive be installed before the old one can be removed, I’m effectively forced to either run RAID5 with a hot spare, or throw caution to the wind entirely and rely solely on node mirroring to protect against drive failures.
Not… super helpful. I suppose the question I’d like answered is “will storage spaces throw a hissyfit and trash my entire array if I pull the failed drive and slot in a new one”…
@Andrew:
This looks like a very good conversation to start at the forum so you could get feedback from the STH community.
If your array is full, yes you can remove the degraded disk first and then replace with a new one. But my experience was that you HAD to use powershell to do it. The GUI wouldn’t play nice.
Steps here:
https://hodgkins.io/replace-failed-disk-in-storage-spaces-pool-with-powershell
If your array is full, yes you can replace a degraded disk with a new one. But my experience was that you HAD to use powershell to do it. The GUI wouldn’t play nice.
Steps here:
https://hodgkins.io/replace-failed-disk-in-storage-spaces-pool-with-powershell
The next question for me would be….. “Do not make any changes to the Storage Pool while repair operation is going on.”
Does that mean no data writes? or does that mean no configuration changes?
@Joswa:
The normal operation such as data writes are fine, but please be caution of pool configuration changes. It will be a good idea to verify backup status as well.
Here is for hoping that this reply still gets seen and a helpful response results.
I have a storage pool that I originally configured on win server 2012r2, but when that server boot drive failed like a year ago I replaced it and installed server 2016. The storage pool is a thin’ly provisioned 20TB virtual disk with pairty spread across six 5TB external usb drives (all arranged on a nice looking magazine rack with a gigabyte brix driving the show, cable managed and setup to be a living room staple).
This is what I like to call a production lab, as I try to do things in a production like manner but it is still a lab for my learning benefit and to test things out. However it also acts as a file server and I use it a lot for that.
Anyways the drives are like 6 years old and one of them started making some very ominous sounds (but still reported working fine. So I ordered it’s replacement and it arrived today a upgrade from 5tb to 8tb on the drive. I shut the computer down unplugged the old drive used its connections to plug in the new drive and started futzing with storage pools having never done this before.
Now the 8TB drive is listed as part of the pool, but the 5tb drive that is physically unplugged cannot be removed from the pool nor reset. It complains that I have to replace the drive (but i did), I hit repair virtual drive several times but it completes much to quick to be doing anything. The old 5tb drive are actually using about 3.??TB of their space the new 8TB drive is using about 2 gigs. the get-storagejob command returns literally nothing but a new prompt.
I cannot remove either the 8tb or the 5tb drive from the pool because it wants a replacement drive when the 8tb drive was supposed to be //the replacement//.
Helps please