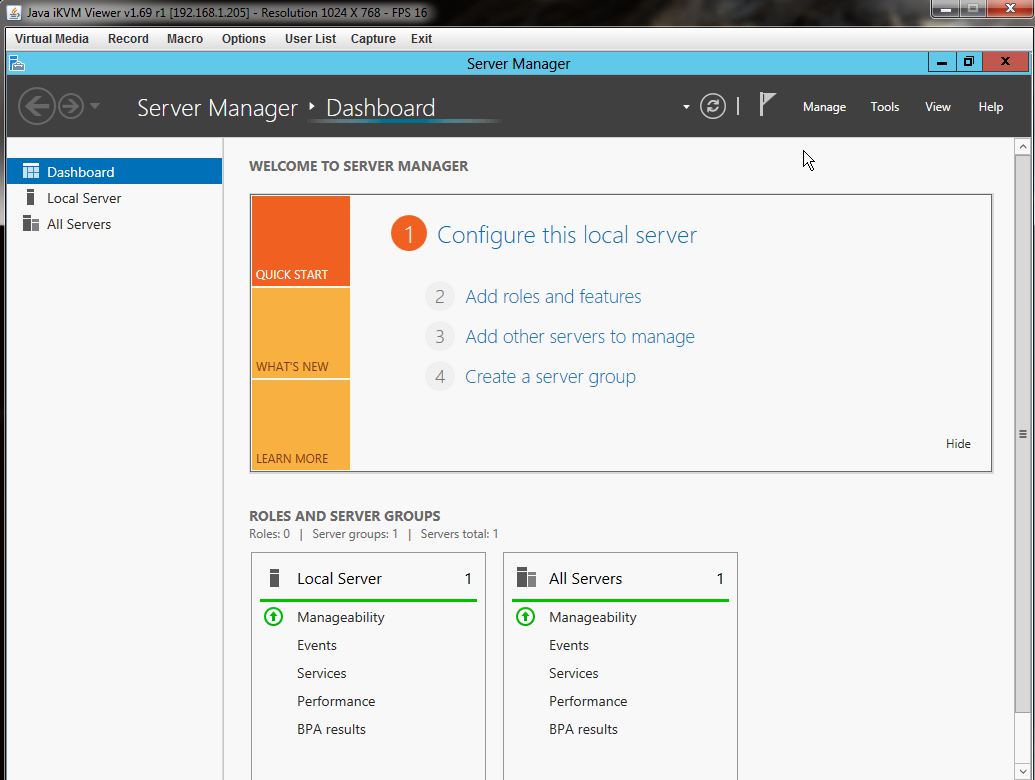
We published a how to guide video on resetting a Windows Server 2012 R2 Administrator password remotely using IPMI. If you have ever had a Windows Server machine where you could not access the machine due to a lost password, this is the way to recover the system without resorting to a 3rd party password reset tool that can potentially be plagued with malware.
Recently we had a test running on a 24 drive SSD system in the STH lab. This is a system that will be available on the public DemoEval program after Flash Memory Summit with 24 new SSDs. The Administrator password for the Windows installation was lost, and the IOmeter logs inaccessible.
It is extremely important that you reset the Administrator password AND replace the sethc.exe after completing the swap. Otherwise, someone with IPMI access to the machine could gain Administrator access.
Here are the steps:
- Over IPMI, mount a Windows Server 2012 R2 installation disk (this can be found on Microsoft Technet Evaluation Center)
- Reboot the server
- Select Boot from CD/DVD media and start the Windows Server boot process
- Select a language then Repair your computer -> Troubleshoot -> Command Prompt
- Locate the Windows installation drive (C, D or others depending on installation type)
- Copy the sethc.exe to a backup location
- Replace sethc.exe with cmd.exe
- Reboot the server
- At the login screen, hit the SHIFT key five times (you can use the virtual keyboard for this)
- Use the following command (replace <password> with a temporary password) to reset the Administrator password:
net user Administrator <password> - Login using the temporary password
- Reset the password from the Windows Server environment
- Replace the sethc.exe with the backed-up version.
Key commands for steps 6 and 7 (the d:\ may be c:\ or something else based on your step 5 determination):
copy d:\windows\system32\sethc.exe d:\windows\system32\sethc-old.exe
copy d:\windows\system32\cmd.exe d:\windows\system32\sethc.exe
Key commands for step 13:
copy c:\windows\system32\sethc-old.exe c:\windows\system32\sethc.exe
This is all you need to get back into a Windows Server 2012 R2 system you have IPMI access to.
Final Words
Even if you never have to recover a lost Windows Server Administrator password using this methodology, it should be eye-opening. Modern servers do include iKVM functionality with the ability to remotely mount ISO images. This entire operation can occur over a period of a few minutes and leaves the system vulnerable if the sethc.exe is not replaced. Our suggestion is to use a separate network or vlan for all IPMI interfaces.

Seems like this hack applies to anyone who has access to the unencrypted bits of the disk, outside of any permissions applied by the OS. I know there are Linux live CDs out there that include tools targeted for recovering the password. If you have full write access to the disk, you can just replace the password with whatever one you want, I believe. Just need to know where to put it, which isn’t a secret.
The same applies to any who has access to your VMs. If you have access to either the machine running the VM, or the storage where the VM disks are kept, then you can essentially pwn any valuable assets the VMs hold.
Unless, that is, you have taken steps to encrypt/protect the VM and virtual disks. Have you looked into Microsoft’s new Guarded Fabric and Shielded VM technology? You can even set this up to go back to a hardware root of trust, via TPM 2.0. I am trying to find a server that supports TPM 2.0 so I can play around with this. I have a support question out to SuperMicro on whether or not their Xeon-D miniITX line supports it,
FYI, Ireceived confirmation from SuperMicro (via WiredZone) that at least the X10SDV-TLN4F does support TPM 2.0. The appropriate module is the OM-TPM-9665V-S (or possibly AOM-TPM-9665H-S for a pizza box server)
Small correction.
It should be net user not set user.
Thanks! Corrected. Video had it correct :-)
This trick is really clever but it may work with local account only. To reset a forgotten domain password, I have to use pcunlocker.